Effects of media use, smart phone addiction, and adult ADHD symptoms on wellbeing of college students during the COVID-19 lockdown: Dispositional hope as a protective factor
- PMID: 36619067
- PMCID: PMC9816392
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1019976
Effects of media use, smart phone addiction, and adult ADHD symptoms on wellbeing of college students during the COVID-19 lockdown: Dispositional hope as a protective factor
Abstract
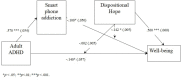
Introduction: The present study investigated the role of dispositional hope as a potential protective factor moderator in the relationship between adult ADHD symptoms, media use/smart phone addiction and wellbeing during the period of isolation because of the COVID-19 pandemic among students in Romania.
Methods: A sample of 333 college students (86.8% female and 13.2% male) between the age of 18 and 47 with a mean of 20.6 years old from West University of Timişoara completed online surveys. Mediation and moderation analyses were performed to assess the associations among the variables.
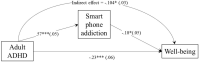
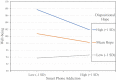
Results: Results confirmed the negative associations of both adult ADHD and smartphone addiction with overall wellbeing. The smartphone addiction/ wellbeing association was moderated by dispositional hopefulness, such that high hopefulness served as a protective factor [b = -0.008, 95% percentile CI (-0.0134; -0.0012)].
Discussion: Implications for the educational environment are discussed.
Keywords: ADHD; college students; hope; smart phone addiction; wellbeing.
Copyright © 2022 Toma, Anderson, Matichescu, Franţ, Almǎjan-Guţă, Cândea and Bailey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson E. L., Steen E., Stavropoulos V. (2017). Internet use and problematic Internet use: a systematic review of longitudinal research trends in adolescence and emergent adulthood. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 22, 430–454. 10.1080/02673843.2016.1227716 - DOI
-
- Arrivillaga C., Rey L., Extremera N. (2020). Adolescents' problematic internet and smartphone use is related to suicide ideation: does emotional intelligence make a difference? Comput. Human Behav. 110, 106375. 10.1016/j.chb.2020.106375 - DOI
-
- Bender P. K., Kim E. L., Gentile D. A. (2020). Gaming disorder in children and adolescents: risk factors and preventive approaches. Curr. Addict. Rep. 7, 553–560. 10.1007/s40429-020-00337-5 - DOI
-
- Brand M., Young K. S., Laier C., Wölfling K., Potenza M. N. (2016). Integrating psychological and neurobiological considerations regarding the development and maintenance of specific Internet-use disorders: an interaction of person-affect-cognitionexecution (I-PACE) model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 71, 252–266. 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.08.033 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

