Advanced technologies for molecular diagnosis of cancer: State of pre-clinical tumor-derived exosome liquid biopsies
- PMID: 36619206
- PMCID: PMC9812720
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100538
Advanced technologies for molecular diagnosis of cancer: State of pre-clinical tumor-derived exosome liquid biopsies
Abstract
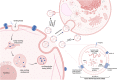
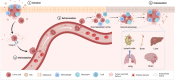
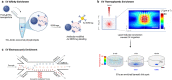
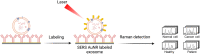
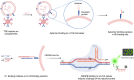
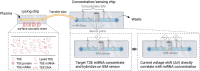
Exosomes are membrane-defined extracellular vesicles (EVs) approximately 40-160 nm in diameter that are found in all body fluids including blood, urine, and saliva. They act as important vehicles for intercellular communication between both local and distant cells and can serve as circulating biomarkers for disease diagnosis and prognosis. Exosomes play a key role in tumor metastasis, are abundant in biofluids, and stabilize biomarkers they carry, and thus can improve cancer detection, treatment monitoring, and cancer staging/prognosis. Despite their clinical potential, lack of sensitive/specific biomarkers and sensitive isolation/enrichment and analytical technologies has posed a barrier to clinical translation of exosomes. This review presents a critical overview of technologies now being used to detect tumor-derived exosome (TDE) biomarkers in clinical specimens that have potential for clinical translation.
Keywords: Cancer; Enrichment; Exosome; Isolation; Laboratory developed tests; Molecular diagnosis.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Gutman S. Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH); 2004. Evaluation of Automatic Class III Designation CellSearch Epithelial Cell Kit/cell Spotter Analyzer. K031588.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

