High precision but systematic offset in a standing bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) compared with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA)
- PMID: 36619314
- PMCID: PMC9813632
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjnph-2022-000512
High precision but systematic offset in a standing bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) compared with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA)
Abstract
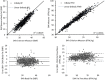
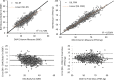
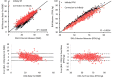
Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) provides a practical method of body composition estimation for field research and weight management programmes, with devices and algorithms that have improved in recent years. We compared suitability of a commercial BIA system that uses multi-frequency-based proprietary algorithms (InBody 770, Cerritos, California, USA) and a laboratory-based validated single-frequency system (Quantum IV, RJL Systems, Clinton Township, Michigan, USA) with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) (iDXA, GE Lunar, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). Volunteers included fit non-obese active duty US Marines (480 men; 315 women), assessed by DXA and the two BIA systems. Both RJL and InBody BIA devices predicted DXA-based fat-free mass (FFM) (mean absolute error (MAE) 2.8 and 3.1 kg, respectively) and per cent body fat (%BF) (MAE 3.4% and 3.9%, respectively), with higher correlations from the InBody device (r2=0.96 (%BF) and 0.84 (FFM)) versus the RJL (r2=0.92 (%BF) and 0.72 (FFM)). InBody overpredicted FFM (bias +2.7, MAE 3.1 kg) and underpredicted %BF (bias -3.4 and MAE 3.9%) versus the RJL. A 3% correction factor applied to the InBody device results provided values very close to the DXA measurements. These findings support the application of modern BIA systems to body composition goals of maximum %BF and minimum lean body mass for both men and women.
Keywords: Nutrition assessment; Physical performance; Weight management.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Agreement Between 2 Segmental Bioimpedance Devices, BOD POD, and DXA in Obese Adults.J Clin Densitom. 2020 Jan-Mar;23(1):138-148. doi: 10.1016/j.jocd.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 Apr 27. J Clin Densitom. 2020. PMID: 31122829
-
Comparison of body composition by bioelectrical impedance and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry in overweight/obese postmenopausal women.J Clin Densitom. 2009 Apr-Jun;12(2):238-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jocd.2009.01.004. Epub 2009 Mar 13. J Clin Densitom. 2009. PMID: 19285894
-
Reliability, biological variability, and accuracy of multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis for measuring body composition components.Front Nutr. 2024 Dec 3;11:1491931. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1491931. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39691170 Free PMC article.
-
Circumference-Based Predictions of Body Fat Revisited: Preliminary Results From a US Marine Corps Body Composition Survey.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 31;13:868627. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.868627. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35432005 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Review of the Correlations of Measurement Parameters among Modern Technologies for Sarcopenia Assessment.Aging Dis. 2025 May 22. doi: 10.14336/AD.2025.0145. Online ahead of print. Aging Dis. 2025. PMID: 40479576 Review.
Cited by
-
Big data-based reference centiles for body composition in Korean children and adolescents: a cross-sectional study.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Oct 30;24(1):692. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05166-3. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39478496 Free PMC article.
-
Phase angle and extracellular water-to-total body water ratio estimated by bioelectrical impedance analysis are associated with levels of hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients with diabetes.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 21;9(4):e14724. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14724. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37057050 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of postoperative long-term skeletal muscle mass reduction after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer.Esophagus. 2025 Jul 24. doi: 10.1007/s10388-025-01145-4. Online ahead of print. Esophagus. 2025. PMID: 40707773
-
Phase angle at bioelectric impedance analysis is associated with detrimental sperm quality in idiopathic male infertility: a preliminary clinical study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Apr 24;15:1354733. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1354733. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38721147 Free PMC article.
-
Defining Overweight and Obesity by Percent Body Fat Instead of Body Mass Index.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Mar 17;110(4):e1103-e1107. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae341. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 38747476 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thomasset MA. [Bioelectric properties of tissue. Impedance measurement in clinical medicine. Significance of curves obtained]. Lyon Med 1962;94:107–18. - PubMed
-
- Nyboer J. Electrical impedance plethysmography. In: Thomas CC, ed. Springfield, ill, 1959.
-
- Moore FD. The body cell mass and its supporting environment. London: W.B. Saunders, 1963.
-
- Mills W, Rau D. University of Alaska high latitude study, and the MT. McKinley project, 1981-1983. Alaska Med 1983;25:21–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
