A novel prognostic model to predict OS and DFS of stage II/III gastric adenocarcinoma patients in China
- PMID: 36619400
- PMCID: PMC9812716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12403
A novel prognostic model to predict OS and DFS of stage II/III gastric adenocarcinoma patients in China
Abstract
Background: The prognosis of advanced gastric adenocarcinoma (GAC) after radical gastrectomy varies greatly. We aimed to build and validate a novel individualized nomogram based on inflammation index and tumor markers for patients with stage II/III GAC.
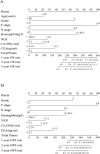
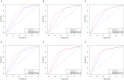
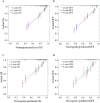
Methods: A total of 755 individuals with stage II/III GAC who had undergone radical gastrectomy at the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University between 2012 and 2017 were included in this retrospective study. The patients were randomly divided into a training cohort (n = 503) and a validation cohort (n = 252). Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to determine independent prognostic factors of overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS). A nomogram was developed based on these independent factors. The concordance index (C-index) and calibration curves were used to evaluate the predictive accuracy of the nomogram.
Results: Univariate and multivariate analyses demonstrated that older age, poor differentiation, advanced stage, elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), lower hemoglobin, and high carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) levels were significantly associated with lower OS and DFS and were independent prognostic factors in stage II/III GAC. The nomogram developed based on these factors in the training cohort showed excellent calibration and discrimination (OS: C-index = 0.739, 95% CI = 0.706-0.772; DFS: C-index = 0.735, 95% CI = 0.702-0.769). In the internal validation cohort, the nomogram was also well-calibrated for the prediction of OS and DFS; it was superior to the 8th edition UICC/AJCC TNM staging system (for OS: C-index = 0.746 vs. 0.679, respectively; for DFS: C-index = 0.736 vs. 0.675, respectively; P < 0.001).
Conclusion: The nomogram model could reliably predict OS and DFS in stage II/III gastric cancer patients with radical gastrectomy. It may help physicians make better treatment decisions.
Keywords: Gastric adenocarcinoma; Inflammatory index; Nomogram; Prognosis; Tumor markers.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Relationship between preoperative inflammatory indexes and prognosis of patients with rectal cancer and establishment of prognostic nomogram prediction model].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022 May 23;44(5):402-409. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20200630-00612. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35615796 Chinese.
-
Clinical value and application of a novel nomogram containing inflammatory, nutritional and clinical markers in predicting overall survival of stage II/III gastric cancer patients after radical resection: a bi-centered retrospective study of 2,443 patients.Am J Transl Res. 2022 Jul 15;14(7):5107-5115. eCollection 2022. Am J Transl Res. 2022. PMID: 35958492 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Clinicopathological Characteristics and Development of an Individualized Prognostic Model for Patients With Hepatoid Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Oct 1;4(10):e2128217. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.28217. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34609494 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram Based on Systemic Immune-Inflammation Index to Predict Survival of Tongue Cancer Patients Who Underwent Cervical Dissection.Front Oncol. 2020 Mar 11;10:341. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00341. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32219070 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment of a prognostic nomogram to predict long-term survival in non-metastatic colorectal cancer patients].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017 Jun 25;20(6):654-659. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28643310 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Prediction models for the survival in patients with intestinal-type gastric adenocarcinoma: a retrospective cohort study based on the SEER database.BMJ Open. 2023 Apr 19;13(4):e070803. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-070803. BMJ Open. 2023. PMID: 37076155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R.L., et al. Global cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Ajani J.A., Lee J., Sano T., et al. Gastric adenocarcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017;3 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

