Scedosporium apiospermum invasive rhinosinusitis in an elderly patient: diagnosis and treatment
- PMID: 36619462
- PMCID: PMC9813714
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12476
Scedosporium apiospermum invasive rhinosinusitis in an elderly patient: diagnosis and treatment
Abstract
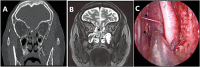
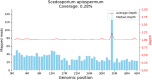
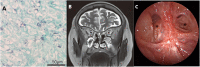
Scedosporium apiospermum is a ubiquitous organism present in the environment and is rarely identified in rhinosinusitis. We report a case of invasive rhinosinusitis with Scedosporium apiospermum which made a definite diagnosis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) from a biopsy sample. The resection of the Scedosporium apiospermum pathological mass was performed with low-temperature plasma radiofrequency ablation. Six months of continuous oral voriconazole treatment was followed. The patient was asymptomatic with no signs of recurrence during the next 1-year follow-up.
Keywords: Invasive fungal rhinosinusitis; Metagenomic next-generation sequencing; Scedosporium apiospermum.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systemic Scedosporium apiospermum Infection Affecting Multiple Sites After Near-Drowning: A Case Report.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Dec 20;17:5739-5744. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S483524. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39720616 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis of pulmonary Scedosporium apiospermum infection from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid by metagenomic next-generation sequencing in an immunocompetent female patient with normal lung structure: a case report and literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Mar 13;24(1):308. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09140-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38481149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-organ involvement caused by Scedosporium apiospermum infection after near drowning: a case report and literature review.BMC Neurol. 2024 Apr 15;24(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03637-9. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38616262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A systemic infection involved in lung, brain and spine caused by Scedosporium apiospermum species complex after near-drowning: a case report and literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Mar 21;24(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08279-9. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38515075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scedosporium apiospermum as a rare cause of fungal rhinosinusitis.J Family Med Prim Care. 2019 Feb;8(2):766-768. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_434_18. J Family Med Prim Care. 2019. PMID: 30984713 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systemic Scedosporium apiospermum Infection Affecting Multiple Sites After Near-Drowning: A Case Report.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Dec 20;17:5739-5744. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S483524. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39720616 Free PMC article.
-
Scedosporiosis and lomentosporiosis: modern perspectives on these difficult-to-treat rare mold infections.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024 Jun 13;37(2):e0000423. doi: 10.1128/cmr.00004-23. Epub 2024 Mar 29. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38551323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perichondritis of the auricle: bacterial or fungal? (A case series).Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Oct;281(10):5559-5562. doi: 10.1007/s00405-024-08792-w. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38977484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swami T., Pannu S., Kumar M., Gupta G. Chronic invasive fungal rhinosinusitis by Paecilomyces variotii: a rare case report. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2016;34(1):103–106. - PubMed
-
- deShazo R.D., O'Brien M., Chapin K., Soto-Aguilar M., Gardner L., Swain R. A new classification and diagnostic criteria for invasive fungal sinusitis. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1997;123(11):1181–1188. - PubMed
-
- Fung M., Babik J., Humphreys I.M., Davis G.E. Diagnosis and treatment of acute invasive fungal sinusitis in cancer and transplant patients. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2019;21(12):53. - PubMed
-
- Alarifi I., Alsaleh S., Alqaryan S., Assiri H., Alsukayt M., Alswayyed M., et al. Chronic granulomatous invasive fungal sinusitis: a case series and literature review. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021;100(5_suppl):720S–727S. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

