The clinical value of angiopoietin-2 in liver diseases
- PMID: 36619892
- PMCID: PMC9815690
- DOI: 10.1002/cld.1218
The clinical value of angiopoietin-2 in liver diseases
Abstract
Content available: Audio Recording.
© 2022 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to report.
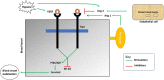
Figures
Similar articles
-
Angiopoietin-2 Serum Levels Improve Noninvasive Fibrosis Staging in Chronic Hepatitis C: A Fibrogenic-Angiogenic Link.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 18;8(6):e66143. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066143. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23823085 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial angiopoietin-2 overexpression in explanted livers identifies subjects at higher risk of recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 8;12:960808. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.960808. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36158651 Free PMC article.
-
Angiopoietin-2 in acute liver failure.Crit Care Med. 2012 May;40(5):1499-505. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318241e34e. Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22430236
-
Circulating angiopoietin-like proteins in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lipids Health Dis. 2021 May 25;20(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01481-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2021. PMID: 34034750 Free PMC article.
-
THE ANGIOPOIETIN/TIE PATHWAY IN RETINAL VASCULAR DISEASES: A Review.Retina. 2021 Jan 1;41(1):1-19. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000003003. Retina. 2021. PMID: 33136975 Review.
Cited by
-
Current and novel biomarkers in cardiogenic shock.Eur J Heart Fail. 2025 Jun;27(6):1106-1125. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.3531. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Eur J Heart Fail. 2025. PMID: 39822053 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multivariate protein landscape of host response in hospitalised patients with suspected infection in the emergency department.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 22;16(1):7848. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62848-x. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40846700 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yamashita S, Kudo A, Kawakami H, Okada Y. Mechanisms of angiogenic suppression in uteri exposed to diethylstilbestrol neonatally in the mouse. Biol Reprod. 2013;88:116. - PubMed
-
- Lefere S, Van de Velde F, Hoorens A, Raevens S, Van Campenhout S, Vandierendonck A, et al. Angiopoietin‐2 promotes pathological angiogenesis and is a therapeutic target in murine nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2019;69:1087–104. - PubMed
-
- Olsson A‐K, Dimberg A, Kreuger J,Claesson‐Welsh L. VEGF receptor signalling ‐ in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:359–71. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

