The use of filamentous hemagglutinin adhesin to detect immune responses to Campylobacter hepaticus infections in layer hens
- PMID: 36619951
- PMCID: PMC9811313
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1082358
The use of filamentous hemagglutinin adhesin to detect immune responses to Campylobacter hepaticus infections in layer hens
Abstract
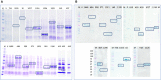
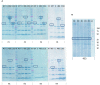
Campylobacter hepaticus is the aetiological agent of Spotty Liver Disease (SLD). SLD can cause significant production loss and mortalities among layer hens at and around peak of lay. We previously developed an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), SLD-ELISA1, to detect C. hepaticus specific antibodies from bird sera using C. hepaticus total proteins and sera pre-absorbed with Campylobacter jejuni proteins. The high specificity achieved with SLD-ELISA1 indicated the presence of C. hepaticus specific antibodies in sera of infected birds. However, some of the reagents used in SLD-ELISA1 are time consuming to prepare and difficult to quality control. This understanding led to the search for C. hepaticus specific immunogenic proteins that could be used in recombinant forms as antibody capture antigens in immunoassay design. In this study, an immunoproteomic approach that combined bioinformatics analysis, western blotting, and LC MS/MS protein profiling was used, and a fragment of filamentous hemagglutinin adhesin (FHA), FHA1,628-1,899 with C. hepaticus specific antigenicity was identified. Recombinant FHA1,628-1,899 was used as antigen coating on ELISA plates to capture FHA1,628-1,899 specific antibodies in sera of infected birds. SLD-ELISA2, based on the purified recombinant FHA fragment, is more user-friendly and standardizable than SLD-ELISA1 for screening antibody responses to C. hepaticus exposure in hens. This study is the first report of the use of FHA from a Campylobacter species in immunoassays, and it also opens future research directions to investigate the role of FHA in C. hepaticus pathogenesis and its effectiveness as a vaccine candidate.
Keywords: Campylobacter hepaticus; ELISA; Spotty Liver Disease; filamentous hemagglutinin adhesion; immunoassay; sera.
Copyright © 2022 Muralidharan, Quinteros, Anwar, Wilson, Scott, Moore and Van.
Conflict of interest statement
JQ, AA, TW, and PS were employed by Scolexia Pty Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detecting Campylobacter hepaticus specific antibodies in chicken sera - a key tool in Spotty Liver Disease screening and vaccine development.Avian Pathol. 2020 Dec;49(6):658-665. doi: 10.1080/03079457.2020.1813252. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Avian Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32835491
-
Prevalence of Campylobacter hepaticus specific antibodies among commercial free-range layers in Australia.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Nov 14;9:1058110. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1058110. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36452145 Free PMC article.
-
Campylobacter hepaticus in the Production Environment and Stagnant Water as a Potential Source of C. hepaticus Causing Spotty Liver Disease in Free-Range Laying Hens in Georgia, United States.Avian Dis. 2023 Mar;67(1):73-79. doi: 10.1637/aviandiseases-D-22-00061. Avian Dis. 2023. PMID: 37140114
-
A review of the novel thermophilic Campylobacter, Campylobacter hepaticus, a pathogen of poultry.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019 Jul;66(4):1481-1492. doi: 10.1111/tbed.13229. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2019. PMID: 31081981 Review.
-
Spotty Liver Disease: A review of an ongoing challenge in commercial free-range egg production.Vet Microbiol. 2018 Dec;227:112-118. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2018.08.004. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Vet Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30473340 Review.
References
-
- Van TTH, Lacey JA, Vezina B, Phung C, Anwar A, Scott PC, et al. . Survival mechanisms of Campylobacter hepaticus identified by genomic analysis and comparative transcriptomic analysis of in vivo and in vitro derived bacteria. Front Microbiol. (2019) 10:107. 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00107 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grimes T, Reece R, editors. “Spotty Liver Disease” – An emerging disease in free range egg layers in Australia. In: Proceedings of the Sixtieth Western Poultry Disease Conference. Sacramento, CA; (2011).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

