The effect of oregano essential oil on the prevention and treatment of Salmonella pullorum and Salmonella gallinarum infections in commercial Yellow-chicken breeders
- PMID: 36619954
- PMCID: PMC9812558
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1058844
The effect of oregano essential oil on the prevention and treatment of Salmonella pullorum and Salmonella gallinarum infections in commercial Yellow-chicken breeders
Abstract
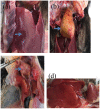
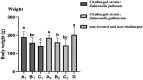
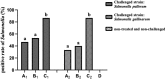
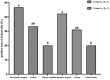
In order to prevent pullorum disease and fowl typhoid in breeders, the use of oregano essential oil (OEO) was tested for the prevention and treatment of infections of multidrug-resistant Salmonella pullorum (SP) and Salmonella gallinarum (SG) in commercial Yellow-chicken breeders. In the challenge-protection experiment, commercial Hongguang-Black 1-day-old breeder chicks were randomly divided into four groups, including A (challenged, preventive dose), B (challenged, treatment dose), C (challenged, untreated), and D (unchallenged, untreated). Group A was supplemented with 200 μL/L OEO in the drinking water during the whole trial (1-35 days of age) and group B was supplemented with 400 μL/L OEO during 8-12 days of age, while groups C and D were kept as untreated controls. At 7 days of age, birds of groups A, B, and C were divided into two subgroups with equal number of birds (A1-A2, B1-B2, and C1-C2), and then subgroups A1, B1, and C1 were challenged with SP, while subgroups A2, B2, and C2 were challenged with SG. Clinical symptoms and death were observed and recorded daily. Every week during the experiment, serum antibodies against SP and SG of all the groups were detected by the plate agglutinate test (PAT). At the age of 35 days, all birds were weighed and necropsied, lesions were recorded and the challenging pathogens were isolated. The results showed that the positive rates of SP and SG isolation in groups A1, A2 and B1, B2 were significantly lower (P < 0.05) than those of groups C1 and C2, respectively, while groups A1 and A2 were slightly lower (P > 0.05) than those of groups B1 and B2. The average body weight (BW) of groups A1 and A2 were significantly higher (P < 0.05) than those of groups B1, B2 and C1, C2, respectively, but there was no significant difference (P > 0.05) with that of group D. The r-value between PAT positive and the recovery rates of Salmonella was 0.99, which means they are highly positively correlated. The results of this study demonstrated that the prevention dose (200μL/L) and the treatment dose (400 μL/L) of OEO supplemented in the drinking water could all effectively decrease infections of SP and SG and that the effect of the prevention was greater than that of the treatment and finally that the prevention could also significantly reduce the BW decline of birds challenged with SP and SG.
Keywords: S. gallinarum; S. pullorum; antibiotic alternatives; body weight; oregano essential oil.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Wang, Li, Wang, Chen, Zhou and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of a selected yeast fraction on the prevention of pullorum disease and fowl typhoid in commercial breeder chickens.Poult Sci. 2020 Jan;99(1):101-110. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez567. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32416790 Free PMC article.
-
[In vitro effect of alendronate on chondrocytes and articular cartilage and subchondral bone in rabbit anterior cruciate ligament transection model].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009 Dec;23(12):1474-81. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009. PMID: 20073314 Chinese.
-
Control of Salmonella Enteritidis and Salmonella Gallinarum in birds by using live vaccine candidate containing attenuated Salmonella Gallinarum mutant strain.Vaccine. 2010 Apr 1;28(16):2853-9. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.01.058. Epub 2010 Feb 11. Vaccine. 2010. PMID: 20153354
-
Immunoprophylaxis of Salmonella gallinarum infection by Salmonella enteritidis-immune lymphokines in broiler chicks.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997;412:413-20. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-1828-4_64. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1997. PMID: 9192048 Clinical Trial.
-
Fowl typhoid and pullorum disease.Rev Sci Tech. 2000 Aug;19(2):405-24. doi: 10.20506/rst.19.2.1222. Rev Sci Tech. 2000. PMID: 10935271 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Hidden Mechanism: How LuxS/AI-2 quorum sensing system drives antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella pullorum through activation of the efflux pump AcrAB-TolC.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):104972. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104972. Epub 2025 Mar 7. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40056776 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella Infection in Poultry: A Review on the Pathogen and Control Strategies.Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 20;11(11):2814. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112814. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004824 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress on the prevention of poultry Salmonella with natural medicines.Poult Sci. 2025 Jan;104(1):104603. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104603. Epub 2024 Nov 27. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 39631274 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shi MY Li M, Wang PK, Wang WW Li HJ, Gao YL, et al. . An outbreak in three-yellow chickens with clinical tumors of high mortality caused by the coinfection of reticuloendotheliosis virus and Marek's disease virus: a speculated reticuloendotheliosis virus contamination plays an important role in the case. Poult Sci. (2021) 100:19–25. 10.1016/j.psj.2020.09.034 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wei P. Challenge and development opportunity of quality chicken industry in China: a review about 9 issues on the topic. Chin Poult. (2019) 41:1–6.
-
- Hu C, Dou W, Zhao G. Enzyme immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles electroposition and Streptavidin-biotin system for detection of S. pullorum and S gallinarum. Electrochimica Acta. (2014) 117:239–45. 10.1016/j.electacta.2013.11.132 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

