Prevalence, diagnosis, and manifestations of brucellosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 36619963
- PMCID: PMC9813401
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.976215
Prevalence, diagnosis, and manifestations of brucellosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Brucellosis is one of the most prevalent zoonotic diseases common between humans and animals. Despite eradication efforts, the burden of the disease is well-known in endemic countries and in countries where brucellosis has not been an important health issue until recently. The aim of this study was to evaluate the prevalence, diagnosis, and manifestations of brucellosis.
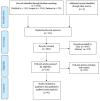
Methods: In this study, PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, and Google scholar databases were systematically searched to find studies published from 2011 to 2021. The search was conducted using text words and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) Terms on the prevalence of brucellosis. Stata software 14.0 was used for all analyses.
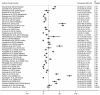
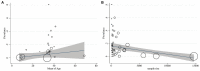
Results: Based on the results, the pooled prevalence of brucellosis was 15.27% (95% CI: 9.68-21.86; heterogeneity I 2 index: 97.43; p < 0.001) for man and 15.33% (95% CI: 7.19-25.75; heterogeneity I 2 index: 98.19; p < 0.001) for woman. Age (coefficient: 0.240; p = 0.480), gender (coefficient: -0.017; p = 0.800), and publication year (coefficient: 0.114; p = 0.861) showed no significant effect on heterogeneity among studies. Egger's test indicated a significant publication bias for the prevalence of brucellosis (coefficient 3.894; p < 0.001). Moreover, the trim-and-fill method exhibited that the adjusted prevalence of brucellosis (18.30%, 95% CI: 14.10-22.52) was not significantly different from the original prevalence of brucellosis.
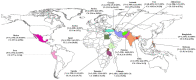
Conclusion: The pooled estimate for brucellosis prevalence was estimated as 15.53%. To better understand the epidemiology of brucellosis globally, more extensive studies are needed to be conducted throughout the world, especially in developing and low-income countries.
Keywords: Brucella; brucellosis; diagnosis; prevalence; review.
Copyright © 2022 Khoshnood, Pakzad, Koupaei, Shirani, Araghi, Irani, Moradi, Pakzad, Sadeghifard and Heidary.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Global Comprehensive Literature Review and Meta-Analysis of Brucella spp. in Swine Based on Publications From 2000 to 2020.Front Vet Sci. 2021 May 7;8:630960. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.630960. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34026886 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of Bovine Brucellosis in Ethiopia: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Vet Med (Auckl). 2021 Jan 12;12:1-6. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S289721. eCollection 2021. Vet Med (Auckl). 2021. PMID: 33469511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology of brucellosis in Iran: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis study.Microb Pathog. 2017 Aug;109:239-247. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.06.005. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28602839
-
Epidemiology of podoconiosis in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol.BMJ Open. 2020 Jan 7;10(1):e032850. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032850. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 31915168 Free PMC article.
-
The burden of brucellosis in donkeys and its implications for public health and animal welfare: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Vet World. 2025 Feb;18(2):367-378. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2025.367-378. Epub 2025 Feb 17. Vet World. 2025. PMID: 40182828 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative clinical studies on antibiotic treatment of brucellosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 16;14(1):19037. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69669-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39152180 Free PMC article.
-
Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in Sheep and Goats With Owners' Knowledge, Attitudes and Practices in Garowe District, Nugal region, Somalia.Environ Health Insights. 2024 Oct 4;18:11786302241287112. doi: 10.1177/11786302241287112. eCollection 2024. Environ Health Insights. 2024. PMID: 39372709 Free PMC article.
-
A case of polycystic kidney disease infection caused by Brucella: report and literature review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 10;12:1613953. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1613953. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40708629 Free PMC article.
-
The Reasons Behind Long-Term Endemicity of Brucellosis in Low and Middle-Income Countries: Challenges and Future Perspectives.Curr Microbiol. 2024 Jan 30;81(3):82. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03605-5. Curr Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38289422 Review.
-
Progress and persistence of diseases of high consequence to livestock in the United States.One Health. 2024 Jul 29;19:100865. doi: 10.1016/j.onehlt.2024.100865. eCollection 2024 Dec. One Health. 2024. PMID: 39185352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

