ML364 exerts the broad-spectrum antivirulence effect by interfering with the bacterial quorum sensing system
- PMID: 36619997
- PMCID: PMC9813848
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.980217
ML364 exerts the broad-spectrum antivirulence effect by interfering with the bacterial quorum sensing system
Abstract
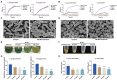
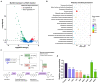
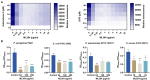
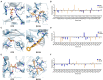
Antivirulence strategy has been developed as a nontraditional therapy which would engender a lower evolutionary pressure toward the development of antimicrobial resistance. However, the majority of the antivirulence agents currently in development could not meet clinical needs due to their narrow antibacterial spectrum and limited indications. Therefore, our main purpose is to develop broad-spectrum antivirulence agents that could target on both Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens. We discovered ML364, a novel scaffold compound, could inhibit the productions of both pyocyanin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and staphyloxanthin of Staphylococcus aureus. Further transcriptome sequencing and enrichment analysis showed that the quorum sensing (QS) system of pathogens was mainly disrupted by ML364 treatment. To date, autoinducer-2 (AI-2) of the QS system is the only non-species-specific signaling molecule that responsible for the cross-talk between Gram-negative and Gram-positive species. And further investigation showed that ML364 treatment could significantly inhibit the sensing of AI-2 or its nonborated form DPD signaling in Vibrio campbellii MM32 and attenuate the biofilm formation across multi-species pathogens including Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus. The results of molecular docking and MM/GBSA free energy prediction showed that ML364 might have higher affinity with the receptors of DPD/AI-2, when compared with DPD molecule. Finally, the in vivo study showed that ML364 could significantly improve the survival rates of systemically infected mice and attenuate bacterial loads in the organs of mice. Overall, ML364 might interfere with AI-2 quorum sensing system to exert broad-spectrum antivirulence effect both in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: ML364; antimicrobial resistance; autoinducer-2; broad-spectrum antivirulence agent; quorum sensing.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Dong, Sun, Hu, Wang, Nie, Li, Wang, Pang, Pang, Lu, Yao and You.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interfering with Bacterial Quorum Sensing.Perspect Medicin Chem. 2016 Jan 18;8:1-15. doi: 10.4137/PMC.S13209. eCollection 2016. Perspect Medicin Chem. 2016. PMID: 26819549 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities of Gliptins against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.Biomedicines. 2022 May 18;10(5):1169. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051169. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625906 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Autoinducer-2 Quorum Sensing Inhibitor on Interspecies Quorum Sensing.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 28;13:791802. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.791802. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35418956 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors: attractive alternatives for control of infectious pathogens showing multiple drug resistance.Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2013 Apr;8(1):68-83. doi: 10.2174/1574891x11308010012. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23394143 Review.
-
Quorum-Sensing Systems as Targets for Antivirulence Therapy.Trends Microbiol. 2018 Apr;26(4):313-328. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Trends Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29132819 Review.
Cited by
-
Design and Synthesis of Novel Antimicrobial Agents.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Mar 22;12(3):628. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12030628. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36978495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of USP2 Enhances TRAIL-Mediated Cancer Cell Death through Downregulation of Survivin.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 15;24(16):12816. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612816. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davis M. I., Pragani R., Fox J. T., Shen M., Parmar K., Gaudiano E. F., et al. . (2016). Small molecule inhibition of the ubiquitin-specific protease USP2 accelerates cyclin D1 degradation and leads to cell cycle arrest in colorectal cancer and mantle cell lymphoma models. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 24628–24640. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.738567, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

