Study on the drug resistance and pathogenicity of Escherichia coli isolated from calf diarrhea and the distribution of virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance genes
- PMID: 36620061
- PMCID: PMC9815963
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.992111
Study on the drug resistance and pathogenicity of Escherichia coli isolated from calf diarrhea and the distribution of virulence genes and antimicrobial resistance genes
Abstract
Introduction: The unscientific and irrational use of antimicrobial drugs in dairy farms has led to the emergence of more serious drug resistance in Escherichia coli.
Methods: In this study, cases of calf diarrhea in cattle farms around the Hohhot area were studied, and Escherichia coli were identified by PCR and biochemical methods, while the distribution of virulence and drug resistance genes of the isolates was analyzed.
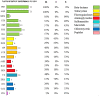
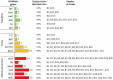
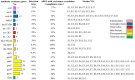
Results: The results showed that 21 strains of Escherichia coli were isolated from the diseased materials, and the isolation rate was 60%. The isolated strains belong to 15 ST types. The drug resistance levels of the isolated strains to 20 kinds of antimicrobial agent viz., penicillin, ampicillin, cefotaxime, cefepime, cefoxitin, and ceftriaxone were more than 50%. The resistance rate to meropenem was 10%. The resistance rates to tetracycline and doxycycline were 33% and 29%, to ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin and enrofloxacin were 48%, 33%, and 33%, to amikacin, kanamycin and gentamicin were 19%, 24% and 38%, to cotrimoxazole and erythromycin were 48% and 15%, to florfenicol, chloramphenicol and polymyxin B were 29%, 33%, and 5%. Nine strains of pathogenic calf diarrhea Escherichia coli were isolated by mouse pathogenicity test. The detection rates of virulence genes for the adhesion class were fimC (95%), IuxS (95%), eaeA (76%), fimA (62%), ompA (52%), and flu (24%). The detection rates for iron transporter protein like virulence genes were iroN (33%), iutA (19%), fyuA (14%), irp5 (9.5%), Iss (9.5%), and iucD (9.5%). The detection rates for toxin-like virulence genes were phoA (90%), Ecs3703 (57%), ropS (33%), hlyF (14%), and F17 (9.5%). The detection rates of tetracycline resistance genes in isolated strains were tetB (29%), tetA (19%) and tetD (14%). The detection rates for fluoroquinolone resistance genes were parC (Y305H, P333S, R355G) (9.5%), gyrA (S83L, D87N) (28%), qnrD (43%), and qnrS (9.5%). The detection rates for β-lactam resistance genes were bla CTX-M (29%), bla TEM (29%), and bla SHV (9.5%). The detection rates for aminoglycoside resistance genes were strA-B (57%), aacC (33%), aac(3')-IIa (29%), and aadAI (24%). The detection rates of chloramphenicol resistance genes floR and sulfa resistance genes sul2 were 24 and 33%.
Conclusion: Pathogenic Escherichia coli causing diarrhea in calves contain abundant virulence genes and antibiotic resistance genes.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; antimicrobial resistance genes; calf diarrhea; drug resistance genes; virulence genes.
Copyright © 2022 Jia, Mao, Liu, Zhang, Cao and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genes Encoding the Virulence and the Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterotoxigenic and Shiga-Toxigenic E. coli Isolated from Diarrheic Calves.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jun 10;12(6):383. doi: 10.3390/toxins12060383. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32532070 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from retail foods in northern Xinjiang, China.Food Sci Nutr. 2020 Mar 21;8(4):2035-2051. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1491. eCollection 2020 Apr. Food Sci Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32328270 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli of the phylogroups A and C in dairy calves with meningitis and septicemia.Microb Pathog. 2022 Feb;163:105378. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105378. Epub 2022 Jan 1. Microb Pathog. 2022. PMID: 34982979
-
Virulence potential of faecal Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy cows and calves on farms in Perm Krai.Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genet Selektsii. 2022 Aug;26(5):486-494. doi: 10.18699/VJGB-22-59. Vavilovskii Zhurnal Genet Selektsii. 2022. PMID: 36128572 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli From Aquaculture Farms and Their Environment in Zhanjiang, China.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Dec 24;8:806653. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.806653. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 35004933 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Emergence of highly virulent and multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli in breeding sheep with pneumonia, Hainan Province, China.Front Microbiol. 2024 Oct 23;15:1479759. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1479759. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39507338 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiotic Resistance Profiles of Escherichia coli and Salmonella spp. Isolated From Dairy Farms and Surroundings in a Rural Area of Western Anatolia, Turkey.Cureus. 2024 Aug 2;16(8):e65996. doi: 10.7759/cureus.65996. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39221349 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and Drug Resistance Profile of Bovine Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolated in Kazakhstan.Pathogens. 2025 Jan 17;14(1):90. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14010090. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 39861051 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Microbial Composition and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles in Dairy Calves with Diarrhea.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 26;15(1):10. doi: 10.3390/life15010010. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39859950 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of ofloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli strains causing calf diarrhea by quorum-sensing acyl-homoserine lactone signaling molecules.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 5;12:1540132. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1540132. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 39974163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Algammal A. M., El-Kholy A. W., Riad E. M., Mohamed H. E., Elhaig M. M., Yousef S. A. A., et al. (2020). Genes encoding the virulence and the antimicrobial resistance in enterotoxigenic and shiga-toxigenic E. coli isolated from Diarrheic Calves. Toxins 12 383–396. 10.3390/toxins12060383 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babus S. D., Bebear C. M., Charron A., Bébéar C., de Barbeyrac B. (1998). Squencing of grase and topoi somerase IV quinolone resistance determining regions of Chamydia trachomatis and characterization of quinolone resistant nlatants obtained in vitro. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 42 2474–2481. 10.1128/AAC.42.10.2474 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belaynehe K. M., Shin S. W., Yoo H. S. (2018). Interrelationship between tetracycline resistance determinants, phylogenetic group affiliation and carriage of class 1 integrons in commensal Escherichia coli isolates from cattle farms. BMC Vet. Res. 14:340. 10.1186/s12917-018-1661-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

