A diagnostic accuracy study comparing RNA LAMP, direct LAMP, and rapid antigen testing from nasopharyngeal swabs
- PMID: 36620063
- PMCID: PMC9813509
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1063414
A diagnostic accuracy study comparing RNA LAMP, direct LAMP, and rapid antigen testing from nasopharyngeal swabs
Abstract
Introduction: During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, the early detection and isolation of individuals infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus disease 2 (SARS-CoV-2) through mass testing can effectively prevent disease transmission. SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid rapid detection based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) may be appropriate to include in testing procedures.
Methods: We used 860 nasopharyngeal specimens from healthcare workers of Huashan Hospital and COVID-19 patients collected from April 7th to 21st, 2022, to assess the clinical diagnostic performance of the LAMP assay marketed by Shanghai GeneSc Biotech and compared it to the result of a rapid antigen test (RAT) head-to-head.
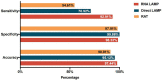
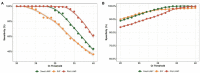
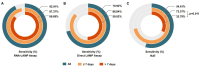
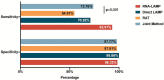
Results: Overall, the diagnostic performance of LAMP assay and RAT were as follows. The LAMP assay represented higher sensitivity and specificity than RAT, especially in the extracted RNA samples. The sensitivity was 70.92% and 92.91% for direct LAMP and RNA-LAMP assay, respectively, while the specificity was 99.86% and 98.33%. The LAMP assay had overall better diagnostic performance on the specimens with relatively lower C t values or collected in the early phase (≤7 days) of COVID-19. The combination of LAMP assay and RAT improved diagnostic efficiency, providing new strategies for rapidly detecting SARS-CoV-2.
Conclusion: The LAMP assay are suitable for mass screenings of SARS-CoV-2 infections in the general population.
Keywords: COVID-19; LAMP assay; SARS-CoV-2; diagnostic accuracy; rapid antigen test.
Copyright © 2022 Cao, Lin, Ai, Cai, Zhang, Yu, Liu, Zhang, Zhang, Fu, Song, Wang, Yuan, Wang, Guan and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development and Clinical Application of a Rapid and Sensitive Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Test for SARS-CoV-2 Infection.mSphere. 2020 Aug 26;5(4):e00808-20. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00808-20. mSphere. 2020. PMID: 32848011 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay as a rapid molecular diagnostic tool for COVID-19 in healthcare workers.J Clin Virol Plus. 2023 Jun;3(2):100134. doi: 10.1016/j.jcvp.2023.100134. Epub 2023 Jan 27. J Clin Virol Plus. 2023. PMID: 36742065 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and the L452R spike mutation using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification plus bioluminescent assay in real-time (RT-LAMP-BART).PLoS One. 2022 Mar 21;17(3):e0265748. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265748. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35312732 Free PMC article.
-
Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays as a rapid diagnostic for COVID-19.Med Hypotheses. 2020 Aug;141:109786. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109786. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 32361529 Free PMC article.
-
A Rapid, Simple, Inexpensive, and Mobile Colorimetric Assay COVID-19-LAMP for Mass On-Site Screening of COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5380. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155380. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751106 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Diagnosis of Zoonotic Malaria.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024 Aug 6;111(4):765-769. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.23-0879. Print 2024 Oct 2. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2024. PMID: 39106849
-
Evaluation of three rapid assays for detecting Mycoplasma pneumoniae in nasopharyngeal specimens.AMB Express. 2024 Dec 18;14(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13568-024-01782-5. AMB Express. 2024. PMID: 39694968 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of the Pluslife Mini Dock RHAM technology with Abbott ID Now and Cepheid GenXpert: A retrospective evaluation study.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 17;14(1):13978. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64406-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38886535 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 RT-LAMP Test.Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023 Jun 13;8(6):320. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed8060320. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37368738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baek Y. H., Um J., Antigua K. J. C., Park J.-H., Kim Y., Oh S., et al. . (2020). Development of a reverse transcription-loop-mediated isothermal amplification as a rapid early-detection method for novel SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 9, 998–1007. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1756698, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

