Liver injury in COVID-19: A minireview
- PMID: 36620342
- PMCID: PMC9813934
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i47.6716
Liver injury in COVID-19: A minireview
Abstract
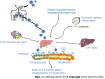
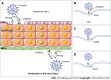
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2), has escalated into a global tragedy afflicting human health, life, and social governance. Through the increasing depth of research and a better understanding of this disease, it has been ascertained that, in addition to the lungs, SARS-CoV-2 can also induce injuries to other organs including the liver. Liver injury is a common clinical manifestation of COVID-19, particularly in severe cases, and is often associated with a poorer prognosis and higher severity of COVID-19. This review focuses on the general existing information on liver injury caused by COVID-19, including risk factors and subpopulations of liver injury in COVID-19, the association between preexisting liver diseases and the severity of COVID-19, and the potential mechanisms by which SARS-CoV-2 affects the liver. This review may provide some useful information for the development of therapeutic and preventive strategies for COVID-19-associated liver injury.
Keywords: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; Chronic liver disease; Liver; SARS-CoV-2; Transmembrane serine protease 2.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19: a fatal case of acute liver failure associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in pre-existing liver cirrhosis.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 3;21(1):901. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06605-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34479499 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of New-Onset Liver Injuries Due to COVID-19 in Preexisting Hepatic Conditions-Review of the Literature.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Dec 28;59(1):62. doi: 10.3390/medicina59010062. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36676691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exposure to particulate matter upregulates ACE2 and TMPRSS2 expression in the murine lung.Environ Res. 2021 Apr;195:110722. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.110722. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Environ Res. 2021. PMID: 33422505 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated FiO2 increases SARS-CoV-2 co-receptor expression in respiratory tract epithelium.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020 Oct 1;319(4):L670-L674. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00345.2020. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32878480 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2: A Potential Target to Prevent COVID-19?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 22;12:725967. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.725967. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34745001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of liver injury in patients with COVID-19.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Jul 21;102(29):e34320. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034320. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37478243 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19, Possible Hepatic Pathways and Alcohol Abuse-What Do We Know up to 2023?Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 12;25(4):2212. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042212. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 Vaccination and Transient Increase in CD4/CD8 Cell Counts in People with HIV: Evidence from China.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 3;12(12):1365. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121365. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39772028 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world data of Azvudine-induced hepatotoxicity among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China: a retrospective case-control study.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 4;16:1558054. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1558054. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40535759 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into COVID-19 associated liver injury: Mechanisms, evaluation, and clinical implications.Hepatol Forum. 2024 Jul 2;5(3):139-149. doi: 10.14744/hf.2023.2023.0025. eCollection 2024. Hepatol Forum. 2024. PMID: 39006140 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berlin DA, Gulick RM, Martinez FJ. Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2451–2460. - PubMed
-
- Santana MF, Guerra MT, Hundt MA, Ciarleglio MM, Pinto RAA, Dutra BG, Xavier MS, Lacerda MVG, Ferreira AJ, Wanderley DC, Borges do Nascimento IJ, Araújo RFA, Pinheiro SVB, Araújo SA, Leite MF, Ferreira LCL, Nathanson MH, Vieira Teixeira Vidigal P. Correlation Between Clinical and Pathological Findings of Liver Injury in 27 Patients With Lethal COVID-19 Infections in Brazil. Hepatol Commun. 2022;6:270–280. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

