Causal Structural Learning on MPHIA Individual Dataset
- PMID: 36620488
- PMCID: PMC9817037
- DOI: 10.1080/01621459.2022.2077209
Causal Structural Learning on MPHIA Individual Dataset
Abstract
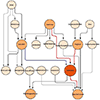
The Population-based HIV Impact Assessment (PHIA) is an ongoing project that conducts nationally representative HIV-focused surveys for measuring national and regional progress toward UNAIDS' 90-90-90 targets, the primary strategy to end the HIV epidemic. We believe the PHIA survey offers a unique opportunity to better understand the key factors that drive the HIV epidemics in the most affected countries in sub-Saharan Africa. In this article, we propose a novel causal structural learning algorithm to discover important covariates and potential causal pathways for 90-90-90 targets. Existing constrained-based causal structural learning algorithms are quite aggressive in edge removal. The proposed algorithm preserves more information about important features and potential causal pathways. It is applied to the Malawi PHIA (MPHIA) data set and leads to interesting results. For example, it discovers age and condom usage to be important for female HIV awareness; the number of sexual partners to be important for male HIV awareness; and knowing the travel time to HIV care facilities leads to a higher chance of being treated for both females and males. We further compare and validate the proposed algorithm using BIC and using Monte Carlo simulations, and show that the proposed algorithm achieves improvement in true positive rates in important feature discovery over existing algorithms.
Keywords: 90-90-90 targets; Causal structural learning; HIV; PHIA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Probabilistic HIV recency classification-a logistic regression without labeled individual level training data.Ann Appl Stat. 2023 Mar;17(1):108-129. doi: 10.1214/22-aoas1618. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Ann Appl Stat. 2023. PMID: 37846343 Free PMC article.
-
Returning HIV-1 viral load results to participant-selected health facilities in national Population-based HIV Impact Assessment (PHIA) household surveys in three sub-Saharan African Countries, 2015 to 2016.J Int AIDS Soc. 2017 Nov;20 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):e25004. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25004. J Int AIDS Soc. 2017. PMID: 29171193 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of travel-time to HIV treatment in sub-Saharan Africa reveals inequities in access to antiretrovirals.Commun Med (Lond). 2025 May 12;5(1):169. doi: 10.1038/s43856-025-00890-y. Commun Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40355703 Free PMC article.
-
[Current status of the female condom in Africa].Sante. 1997 Nov-Dec;7(6):405-15. Sante. 1997. PMID: 9503499 Review. French.
-
The influence of different sexual-contact patterns between age classes on the predicted demographic impact of AIDS in developing countries.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;569:240-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb27374.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989. PMID: 2698092 Review.
References
-
- Bolla Marianna, Abdelkhalek Fatma, and Baranyi Máté. Graphical models, regression graphs, and recursive linear regression in a unified way. Acta Scientiarum Mathematicarum, 85(12): 9–57, 2019.
-
- Bromberg Facundo and Margaritis Dimitris. Improving the reliability of causal discovery from small data sets using argumentation. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 10(12):301–340, 2009.
-
- Colombo Diego and Maathuis Marloes H. Order-independent constraint-based causal structure learning. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 15(1):3741–3782, 2014.
-
- Dawid AP. Conditional independence in statistical theory. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B-Methodological, 41(1):1–15, 1979.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
