LINC00324 in cancer: Regulatory and therapeutic implications
- PMID: 36620587
- PMCID: PMC9815511
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1039366
LINC00324 in cancer: Regulatory and therapeutic implications
Abstract
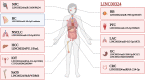
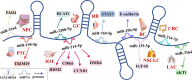
LINC00324 is a 2082 bp intergenic noncoding RNA. Aberrant expression of LINC00324 was associated with the risk of 11 tumors and was closely associated with clinicopathological features and prognostic levels of 7 tumors. LINC00324 can sponge multiple miRNAs to form complex ceRNA networks, and can also recruit transcription factors and bind RNA-binding protein HuR, thereby regulating the expression of a number of downstream protein-coding genes. LINC00324 is involved in 4 signaling pathways, including the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, cell cycle regulatory pathway, Notch signaling pathway, and Jak/STAT3 signaling pathway. High expression of LINC00324 was associated with larger tumors, a higher degree of metastasis, a higher TNM stage and clinical stage, and shorter OS. Currently, four downstream genes in the LINC00324 network have targeted drugs. In this review, we summarize the molecular mechanisms and clinical value of LINC00324 in tumors and discuss future directions and challenges for LINC00324 research.
Keywords: LINC00324; RNA-Binding Protein; cancer; ceRNA; prognosis; signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2022 Xia, Shen, Wang, Ke, Yan, Li, Zhang and Duan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

