Genome-wide association studies identify miRNA-194 as a prognostic biomarker for gastrointestinal cancer by targeting ATP6V1F, PPP1R14B, BTF3L4 and SLC7A5
- PMID: 36620589
- PMCID: PMC9815773
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1025594
Genome-wide association studies identify miRNA-194 as a prognostic biomarker for gastrointestinal cancer by targeting ATP6V1F, PPP1R14B, BTF3L4 and SLC7A5
Abstract
Background: The dysregulated genes and miRNAs in tumor progression can be used as biomarkers for tumor diagnosis and prognosis. However, the biomarkers for predicting the clinical outcome of gastrointestinal cancer (GIC) are still scarce.
Methods: Genome-wide association studies were performed to screen optimal prognostic miRNA biomarkers. RNA-seq, Ago-HITS-CLIP-seq, western blotting and qRT-PCR assays were conducted to identify target genes of miR-194. Genome-wide CRISPR-cas9 proliferation screening analysis were conducted to distinguish passenger gene and driver gene.
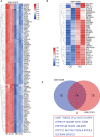
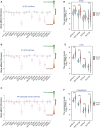
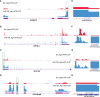
Results: A total of 9 prognostic miRNAs for GIC were identified by global microRNA expression analysis. Among them, miR-194 was the only one miRNA that significantly associated with overall survival, disease-specific survival and progress-free interval in both gastric, colorectal and liver cancers, indicating miR-194 was an optimal prognostic biomarker for GIC. RNA-seq analysis confirmed 18 conservative target genes of miR-194. Four of them, including ATP6V1F, PPP1R14B, BTF3L4 and SLC7A5, were directly targeted by miR-194 and required for cell proliferation. Cell proliferation assay validated that miR-194 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting ATP6V1F, PPP1R14B, BTF3L4 and SLC7A5 in GIC.
Conclusion: In summary, miR-194 is an optimal biomarker for predicting the outcome of GIC. Our finding highlights that miR-194 exerts a tumor-suppressive role in digestive system cancers by targeting ATP6V1F, PPP1R14B, BTF3L4 and SLC7A5.
Keywords: biomarker; gastrointestinal cancer; genome-wide CRISPR-cas9 proliferation screening; miR-194; oncogene; passenger gene.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Xia, Guo, Huang, Wang, Huang, Qin, Leng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

