Early detection of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related subclinical cardiotoxicity: A pilot study by using speckle tracking imaging and three-dimensional echocardiography
- PMID: 36620612
- PMCID: PMC9812579
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1087287
Early detection of immune checkpoint inhibitor-related subclinical cardiotoxicity: A pilot study by using speckle tracking imaging and three-dimensional echocardiography
Abstract
Background: Early detection of subclinical cardiotoxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy can be challenging.
Objective: To evaluate subclinical cardiac dysfunction using two-dimensional speckle tracking imaging (2D-STI) and three-dimensional echocardiography in Chinese patients.
Methods: Fifty-five consecutive patients with malignant tumors treated by immunotherapy were included. They were examined by echocardiography before immunotherapy and after immunotherapy. Left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) was calculated in three-dimensional imaging. Moreover, left ventricular global longitudinal peak systolic strain (LVGLS), left ventricular global circumferential peak systolic strain (LVGCS), right ventricular global longitudinal systolic strain (RVGLS), right ventricular free wall longitudinal peak systolic strain (RVFWLS), and tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) were evaluated. Clinical and laboratory parameters were recorded. Cardiac toxicity events were defined as the presence of heart failure symptoms, LVEF reduction, and increase in troponin. Subclinical cardiac toxicity was defined as cardiac dysfunction associated with ICI treatment, with absent or delayed ICI-associated cardiotoxicity clinical symptoms.
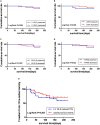
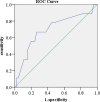
Results: Compared with baseline, the LVGLS, TAPSE, and RVGLS significantly deteriorated after ICI treatment [(-18.63 ± 2.53)% vs. (-17.35 ± 2.58)%, P = 0.000; 18.29 ± 6.23 vs. 14.57 ± 3.81, P = 0.0001; and (-18.45 ± 4.65)% vs. (-14.98 ± 3.85)%, P = 0.0001, respectively]. LVGLS (-17.35 ± 2.58, P = 0.000), TAPSE (14.57 ± 3.81, P = 0.0001), and RVGLS [(-14.98 ± 3.85)%, P = 0.0001] were decreased after ICI immunotherapy. Kaplan-Meier curve analysis showed that LVGLS was more sensitive than the cardiac toxicity events to assess ICI-related subclinical cardiac dysfunction (log-rank P = 0.205). The ROC curve showed that the cutoff value of ΔLVGLS was -13%.
Conclusion: Subclinical cardiac dysfunction can be detected using two-dimensional speckle-tracking imaging. LVGLS, RVGLS, and TAPSE are more sensitive indices for detection.
Clinical trial registration: [https://www.chictr.org.cn/showprojen.aspx?proj=27498], identifier [ChiCTR1800016216].
Keywords: ICIs; TAPSE; echocardiography; strain; subclinical cardiotoxicity.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Yuan, Zhan, Zhao, Mu, Wang, Hu and Fu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Detection of Cardiotoxicity Using Right Ventricular Free Wall Longitudinal Strain in Low Cardiovascular Risk Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Low-Dose Anthracycline Treatment.Cureus. 2024 Jun 25;16(6):e63138. doi: 10.7759/cureus.63138. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39055440 Free PMC article.
-
Application of two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography in radiotherapy-related cardiac systolic dysfunction and analysis of its risk factors: a prospective cohort study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jun 27;24(1):328. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03981-1. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38937716 Free PMC article.
-
[Value of four-dimensional echocardiography combined with speckle tracking technique on the assessment of right heart function and prognosis in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2018 Dec 24;46(12):965-971. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2018.12.007. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 30572401 Chinese.
-
Subclinical systolic dysfunction detected by 2D speckle tracking echocardiography in adults with diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis of 6668 individuals with diabetes mellitus and 7218 controls.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023 May;39(5):977-989. doi: 10.1007/s10554-023-02810-4. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36995526 Free PMC article.
-
The role of stress echocardiography in identifying cardiotoxicity: an in-depth exploration.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 26;11:1236966. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1236966. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38343875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy on biventricular mechanics in cancer patients over a short-term follow-up: a systematic review.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1576175. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1576175. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40547024 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoints in cardiac physiology and pathology: therapeutic targets for heart failure.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024 Jul;21(7):443-462. doi: 10.1038/s41569-023-00986-9. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38279046 Review.
-
Perivascular adipose tissue: a central player in the triad of diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular health.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Dec 28;23(1):455. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02549-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39732729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors-Associated Myocarditis: Diagnosis, Treatment and Current Status on Rechallenge.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 17;12(24):7737. doi: 10.3390/jcm12247737. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38137806 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Complex Connection Between Myocardial Dysfunction and Cancer Beyond Cardiotoxicity: Shared Risk Factors and Common Molecular Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 8;25(23):13185. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313185. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684895 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

