Increased rostral medial frontal GABA+ in early psychosis is obscured by levels of negative affect
- PMID: 36623434
- PMCID: PMC10184492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2022.12.017
Increased rostral medial frontal GABA+ in early psychosis is obscured by levels of negative affect
Keywords: Gamma aminobutyric acid; Magnetic resonance spectroscopy; Psychosis; Schizophrenia.
Figures
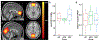
References
-
- de la Fuente-Sandoval C, Reyes-Madrigal F, Mao X, León-Ortiz P, Rodríguez-Mayoral O, Jung-Cook H, Solís-Vivanco R, Graff-Guerrero A, Shungu DC, 2018. Prefrontal and Striatal Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Levels and the Effect of Antipsychotic Treatment in First-Episode Psychosis Patients. Biol. Psychiatry 83, 475–483. 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.09.028 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kegeles LS, Mao X, Stanford AD, Girgis R, Ojeil N, Xu X, Gil R, Slifstein M, Abi-Dargham A, Lisanby SH, Shungu DC, 2012. Elevated prefrontal cortex γ-aminobutyric acid and glutamate-glutamine levels in schizophrenia measured in vivo with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 69, 449–459. 10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.1519 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

