Comprehensive analysis of RNA-binding protein SRSF2-dependent alternative splicing signature in malignant proliferation of colorectal carcinoma
- PMID: 36623729
- PMCID: PMC9926302
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.102876
Comprehensive analysis of RNA-binding protein SRSF2-dependent alternative splicing signature in malignant proliferation of colorectal carcinoma
Abstract
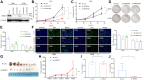
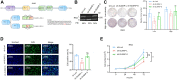
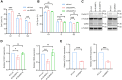
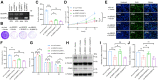
Aberrant expression of serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 2 (SRSF2) can lead to tumorigenesis, but its molecular mechanism in colorectal cancer is currently unknown. Herein, we found SRSF2 to be highly expressed in human colorectal cancer (CRC) samples compared with normal tissues. Both in vitro and in vivo, SRSF2 significantly accelerated the proliferation of colon cancer cells. Using RNA-seq, we screened and identified 33 alternative splicing events regulated by SRSF2. Knockdown of SLMAP-L or CETN3-S splice isoform could suppress the growth of colon cancer cells, predicting their role in malignant proliferation of colon cancer cells. Mechanistically, the in vivo crosslinking immunoprecipitation assay demonstrated the direct binding of the RNA recognition motif of SRSF2 protein to SLMAP and CETN3 pre-mRNAs. SRSF2 activated the inclusion of SLMAP alternative exon 24 by binding to constitutive exon 25, while SRSF2 facilitated the exclusion of CETN3 alternative exon 5 by binding to neighboring exon 6. Knockdown of SRSF2, its splicing targets SLMAP-L, or CETN3-S caused colon cancer cells to arrest in G1 phase of the cell cycle. Rescue of SLMAP-L or CETN3-S splice isoform in SRSF2 knockdown colon cancer cells could effectively reverse the inhibition of cell proliferation by SRSF2 knockdown through mediating cell cycle progression. Importantly, the percentage of SLMAP exon 24 inclusion increased and CETN3 exon 5 inclusion decreased in CRC samples compared to paired normal samples. Collectively, our findings identify that SRSF2 dysregulates colorectal carcinoma proliferation at the molecular level of splicing regulation and reveal potential splicing targets in CRC patients.
Keywords: SRSF2; alternative splicing; colorectal cancer; proliferation.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest All the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of the article.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Serine-arginine splicing factor 2 promotes oesophageal cancer progression by regulating alternative splicing of interferon regulatory factor 3.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):359-367. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2223939. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37335045 Free PMC article.
-
CircPLCE1 facilitates the malignant progression of colorectal cancer by repressing the SRSF2-dependent PLCE1 pre-RNA splicing.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Aug;25(15):7244-7256. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16753. Epub 2021 Jun 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34173324 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of AUF1 alternative splicing by hnRNPA1 and SRSF2 modulate the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Dec;47(6):2349-2366. doi: 10.1007/s13402-024-01023-8. Epub 2024 Dec 9. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 39652302
-
Characterization of RNA-Protein Interactions: Lessons from Two RNA-Binding Proteins, SRSF1 and SRSF2.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1421:1-13. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3591-8_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26965252 Review.
-
Splicing factor SRSF2-centric gene regulation.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Apr 16;17(7):1708-1715. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.58888. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33994855 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biological functions of 5-methylcytosine RNA-binding proteins and their potential mechanisms in human cancers.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 7;15:1534948. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1534948. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39990690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive analysis of splicing factor SRs-related gene characteristics: predicting osteosarcoma prognosis and immune regulation status.Front Oncol. 2024 Sep 2;14:1456986. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1456986. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39286028 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative splicing and related RNA binding proteins in human health and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Feb 2;9(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01734-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38302461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ESRP1-driven alternative splicing of CLSTN1 inhibits the metastasis of gastric cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Dec 19;9(1):464. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01757-8. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 38114495 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring serine-arginine rich splicing factors: potential predictive markers for dysregulation in oral cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Sep 3;24(1):1094. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12750-4. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39227899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou X., Li X., Cheng Y., Wu W., Xie Z., Xi Q., et al. BCLAF1 and its splicing regulator SRSF10 regulate the tumorigenic potential of colon cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:4581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

