Evidence that oncostatin M synergizes with IL-4 signaling to induce TSLP expression in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
- PMID: 36623776
- PMCID: PMC10164690
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2022.11.029
Evidence that oncostatin M synergizes with IL-4 signaling to induce TSLP expression in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
Abstract
Background: Oncostatin M (OSM) may promote type 2 inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) by inducing thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP).
Objective: We sought to study the impact of OSM on TSLP synthesis and release from nasal epithelial cells (NECs).
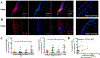
Methods: OSM receptors, IL-4 receptors (IL-4R), and TSLP were evaluated in mucosal tissue and primary NECs from patients with CRSwNP by quantitative PCR and immunofluorescence. Air-liquid interface-cultured NECs were stimulated with cytokines, including OSM, and quantitative PCR, ELISA, Western blot, and flow cytometry were used to assess the expression of OSM receptors, IL-4R, and TSLP.
Results: Increased levels of OSM receptor β chain (OSMRβ), IL-4Rα, and TSLP were observed in nasal polyp tissues and primary epithelial cells from nasal polyps of patients with CRSwNP compared with control tissues or cells from control subjects. The level of expression of OSMRβ in tissue was correlated with levels of both IL-4Rα and TSLP. OSM stimulation of NECs increased the expression of OSMRβ and IL-4Rα. Stimulation with IL-4 plus OSM augmented the production of TSLP; the response was suppressed by a signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 inhibitor. Stimulation of NECs with IL-4 plus OSM increased the expression of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 3, an enzyme that truncates and activates TSLP.
Conclusions: OSM increases the expression of IL-4Rα and synergizes with IL-4 to induce the synthesis and release of TSLP in NECs. Because the combination of IL-4 and OSM also augmented the expression of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin 3, these results suggest that OSM can induce both synthesis and posttranslational processing/activation of TSLP, promoting type 2 inflammation.
Keywords: IL-4Rα; OSM; OSMRβ; TSLP; chronic rhinosinusitis; nasal epithelial cells; nasal polyps; type 2–dominant inflammation.
Copyright © 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest:
PPC, BFW, JN, JP, AIK, LS, RC, JH, DC, KW and ZL report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
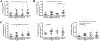
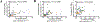



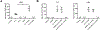

References
-
- Orlandi RR, Kingdom TT, Hwang PH, Smith TL, Alt JA, Baroody FM, et al. International Consensus Statement on Allergy and Rhinology: Rhinosinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 2016; 6 Suppl 1:S22–209. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, Bachert C, Alobid I, Baroody F, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. Rhinol Suppl 2012; 3:1–298. - PubMed
-
- Akdis CA, Bachert C, Cingi C, Dykewicz MS, Hellings PW, Naclerio RM, et al. Endotypes and phenotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis: a PRACTALL document of the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2013; 131:1479–90. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

