Vestibular Complaints Impact on the Long-Term Quality of Life of Vestibular Schwannoma Patients
- PMID: 36624597
- PMCID: PMC9835658
- DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003773
Vestibular Complaints Impact on the Long-Term Quality of Life of Vestibular Schwannoma Patients
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the effect of dizziness-related symptoms on the long-term quality of life (QoL) of patients with unilateral vestibular schwannoma.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, patients with a unilateral vestibular schwannoma diagnosed between 2004 and 2013 completed a disease-specific QoL questionnaire (Penn Acoustic Neuroma Quality of Life [PANQOL]) and the Dizziness Handicap Inventory (DHI) in 2020. Linear regression was performed to assess the correlation between QoL and the DHI total score, and the scores of the DHI functional, emotional, and physical subdomains. Potential confounders such as age, sex, tumor size at baseline, and treatment modality (active surveillance, surgery, or radiotherapy) were included in the model.
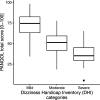
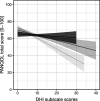
Results: In total, 287 of 479 patients (59%) experienced dizziness with a median follow-up of 10 years. The DHI total score was significantly associated with the PANQOL total score. On average, we found a reduction of 0.7 points on the PANQOL for each additional point on the DHI. The DHI emotional subdomain was the most prominent determinant of poorer QoL. Each point on the DHI emotional subscale was associated with a reduction of 1.3 on the PANQOL score. Treatment modality did not have a clinically relevant effect on dizziness-related QoL.
Conclusions: Even mild dizziness can have a significant and clinically relevant effect on the QoL of patients with unilateral vestibular schwannoma in the long term. This holds true for all treatment modalities. Addressing the vestibular problems may improve QoL in vestibular schwannoma patients, and DHI subscale analysis may help tailor the optimal vestibular intervention.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of Otology & Neurotology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor: "Vestibular Complaints Impact on the Long-Term Quality of Life of Vestibular Schwannoma Patients".Otol Neurotol. 2023 Aug 1;44(7):747. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003943. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Otol Neurotol. 2023. PMID: 37400260 No abstract available.
-
Reply to Letter to the Editor: "Vestibular Complaints Impact on the Long-Term Quality of Life of Vestibular Schwannoma Patients".Otol Neurotol. 2023 Aug 1;44(7):748. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000003944. Epub 2023 Jul 1. Otol Neurotol. 2023. PMID: 37400269 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rosenberg SI. Natural history of acoustic neuromas. Laryngoscope 2000;110:497–508. - PubMed
-
- Jufas N, Flanagan S, Biggs N, Chang P, Fagan P. Quality of life in vestibular schwannoma patients managed by surgical or conservative approaches. Otol Neurotol 2015;36:1245–54. - PubMed
-
- Carlson ML Tveiten ØV Driscoll CL, et al. . What drives quality of life in patients with sporadic vestibular schwannoma? Laryngoscope 2015;125:1697–702. - PubMed
-
- Soulier G van Leeuwen BM Putter H, et al. . Quality of life in 807 Patienst with vestibular schwannoma: comparing treatment modalities. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2017;157:92–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

