Prescribing Trends of Oral Anticoagulants in US Patients With Cirrhosis and Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 36625307
- PMCID: PMC9973619
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.122.026863
Prescribing Trends of Oral Anticoagulants in US Patients With Cirrhosis and Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
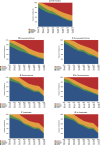
Background Many patients with cirrhosis have concurrent nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF). Data are lacking regarding recent oral anticoagulant (OAC) usage trends among US patients with cirrhosis and NVAF. Methods and Results Using MarketScan claims data (2012-2019), we identified patients with cirrhosis and NVAF eligible for OACs (CHA2DS2-VASc score ≥2 [men] or ≥3 [women]). We calculated the yearly proportion of patients prescribed a direct OAC (DOAC), warfarin, or no OAC. We stratified by high-risk features (decompensated cirrhosis, thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy, chronic kidney disease, or end-stage renal disease). Among 32 487 patients (mean age=71.6 years, 38.5% women, 15.1% with decompensated cirrhosis, mean CHA2DS2-VASc=4.2), 44.6% used OACs within 180 days of NVAF diagnosis, including DOACs (20.2%) or warfarin (24.4%). Compared with OAC nonusers, OAC users were less likely to have decompensated cirrhosis (18.6% versus 10.7%), thrombocytopenia (19.5% versus 12.5%), or chronic kidney disease/end-stage renal disease (15.5% versus 14.0%). Between 2012 and 2019, warfarin use decreased by 21.0% (32.0% to 11.0%), whereas DOAC use increased by 30.6% (7.4% to 38.0%), and among all DOACs between 2012 and 2019, apixaban was the most commonly prescribed (46.1%). Warfarin use decreased and DOAC use increased in all subgroups, including in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis, thrombocytopenia, coagulopathy, chronic kidney disease/end-stage renal disease, and across CHA2DS2-VASc categories. Among OAC users (2012-2019), DOAC use increased by 58.9% (18.7% to 77.6%). Among DOAC users, the greatest proportional increase was with apixaban (61.2%; P<0.001). Conclusions Among US patients with cirrhosis and NVAF, DOAC use has increased substantially and surpassed warfarin, including in decompensated cirrhosis. Nevertheless, >55% of patients remain untreated, underscoring the need for clearer treatment guidance.
Keywords: anticoagulation; atrial fibrillation; cirrhosis; usage.
Figures

References
-
- Beste LA, Leipertz SL, Green PK, Dominitz JA, Ross D, Ioannou GN. Trends in burden of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma by underlying liver disease in US veterans, 2001–2013. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:1471–1482. E1475; quiz e1417‐1478. - PubMed
-
- Chokesuwattanaskul R, Thongprayoon C, Bathini T, O'Corragain OA, Sharma K, Preechawat S, Wijarnpreecha K, Kroner PT, Ungprasert P, Cheungpasitporn W. Epidemiology of atrial fibrillation in patients with cirrhosis and clinical significance: a meta‐analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;31:514–519. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001315 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, Singer DE. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) study. JAMA. 2001;285:2370–2375. doi: 10.1001/jama.285.18.2370 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

