Predictors of stroke or systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation with CHA2 DS2 -VASc score of 0
- PMID: 36625408
- PMCID: PMC10023890
- DOI: 10.1111/anec.13036
Predictors of stroke or systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation with CHA2 DS2 -VASc score of 0
Abstract
Background: Anticoagulant therapy has been important for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF). However, it was not recommended due to its relatively higher risk of bleeding than its lower risk of stroke in patients with a CHA2 DS2 -VASc score of 0.
Hypothesis: This study aimed to evaluate the predictors of stroke in AF patients with very low risk of stroke.
Methods: Between 1990 and 2020, 542 patients with non-valvular AF (NVAF) with a CHA2 DS2 -VASc score of 0 followed up for at least 6 months were enrolled. Patients with only being woman as a risk factor were included as a CHA2 DS2 -VASc score of 0 in this study. The primary outcome was stroke or systemic embolism.
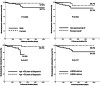
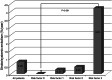
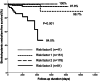
Results: The primary outcome rate was 0.78%/year. In Cox hazard model, age of ≥50 years at diagnosis (hazard ratio [HR] 6.710, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.811-24.860, p = .004), LVEDD of ≥46 mm (HR 4.513, 95% CI 1.038-19.626, p = .045), and non-paroxysmal AF (HR 5.575, 95% CI 1.621-19.175, p = .006) were identified as independent predictors of stroke or systemic embolism. Patients with all three independent predictors had a higher risk of stroke or systemic embolism (4.21%/year), whereas those without did not have a stroke or systemic embolism.
Conclusion: The annual stroke or systemic embolism rate in NVAF patients with CHA2 DS2 -VASc score of 0 was 0.78%/year, and age at AF diagnosis, LVEDD, and non-paroxysmal AF were independent predictors of stroke or systemic embolism in patients considered to have a very low risk of stroke.
Keywords: anticoagulants; atrial fibrillation; risk factors; stroke.
© 2023 The Authors. Annals of Noninvasive Electrocardiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Stroke and systemic embolism risk in patients with CHA2 DS2 -VASc score of 0.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2023 May;28(3):e13060. doi: 10.1111/anec.13060. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2023. PMID: 37060551 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Left atrial function as a predictor of stroke or systemic embolism: Beyond the CHA2 DS2 -VASc score.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2023 Jul;28(4):e13061. doi: 10.1111/anec.13061. Epub 2023 Apr 27. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2023. PMID: 37102456 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Al‐Khatib, S. M. , Thomas, L. , Wallentin, L. , Lopes, R. D. , Gersh, B. , Garcia, D. , Ezekowitz, J. , Alings, M. , Yang, H. , Alexander, J. H. , Flaker, G. , Hanna, M. , & Granger, C. B. (2013). Outcomes of apixaban vs. warfarin by type and duration of atrial fibrillation: Results from the ARISTOTLE trial. European Heart Journal, 34(31), 2464–2471. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin, E. J. , Levy, D. , Vaziri, S. M. , D'Agostino, R. B. , Belanger, A. J. , & Wolf, P. A. (1994). Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population‐based cohort. The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA, 271(11), 840–844. - PubMed
-
- Benz, A. P. , Hijazi, Z. , Lindbäck, J. , Connolly, S. J. , Eikelboom, J. W. , Oldgren, J. , Siegbahn, A. , & Wallentin, L. (2021). Biomarker‐based risk prediction with the ABC‐AF scores in patients with atrial fibrillation not receiving Oral anticoagulation. Circulation, 143(19), 1863–1873. - PubMed
-
- Berg, D. D. , Ruff, C. T. , Jarolim, P. , Giugliano, R. P. , Nordio, F. , Lanz, H. J. , Mercuri, M. F. , Antman, E. M. , Braunwald, E. , & Morrow, D. A. (2019). Performance of the ABC scores for assessing the risk of stroke or systemic embolism and bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation in ENGAGE AF‐TIMI 48. Circulation, 139(6), 760–771. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Citerni, C. , Kirchhoff, J. , Olsen, L. H. , Sattler, S. M. , Gentilini, F. , Forni, M. , Zannoni, A. , Grunnet, M. , Edvardsson, N. , Bentzen, B. H. , & Diness, J. G. (2020). Characterization of atrial and ventricular structural remodeling in a porcine model of atrial fibrillation induced by atrial Tachypacing. Frontiers in Veterinary Science, 7, 179. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

