Dysbiosis of Oral Microbiota and Metabolite Profiles Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 36625596
- PMCID: PMC9927158
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.03796-22
Dysbiosis of Oral Microbiota and Metabolite Profiles Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
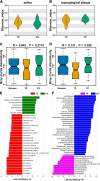
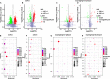
Several previous studies have shown that oral microbial disorders may be closely related to the occurrence and development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, whether the function of oral microorganisms and their metabolites have changed in patients with T2DM who have not suffered from any oral diseases has not been reported. We performed metagenomic analyses and nontargeted metabolic analysis of saliva and supragingival plaque samples from patients with T2DM who have not suffered any oral diseases and normal controls. We found that periodontal pathogens such as Porphyromonas gingivalis and Prevotella melaninogenica were significantly enriched, while the abundances of dental caries pathogens such as Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus were not significantly different in patients with T2DM compared to those in normal controls. Metabolomic analyses showed that the salivary levels of cadaverine and L-(+)-leucine of patients with T2DM were significantly higher than those of normal controls, while the supragingival plaque levels of N-acetyldopamine and 3,4-dimethylbenzoic acid in patients with T2DM were significantly higher than those in the normal controls. Additionally, we identified the types of oral microorganisms related to the changes in the levels of circulating metabolites, and the oral microorganisms were involved in the dysregulation of harmful metabolites such as cadaverine and n, n-dimethylarginine. Overall, our study first described the changes in the composition of oral microorganisms and their metabolites in patients with T2DM who have not suffered any oral diseases, which will provide a direct basis for finding oral biomarkers for early warning of oral diseases in T2DM. IMPORTANCE The incidence of oral diseases in type 2 diabetic patients might increase, and the severity might also be more serious. At present, the relationship between oral microorganisms and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has become a hot topic in systemic health research. However, whether the function of oral microorganisms and their metabolites have changed in patients with T2DM who have not suffered from any oral diseases has not been reported. We found that even if the oral condition of T2DM is healthy, their oral microbes and metabolites have changed, thus increasing the risk of periodontal disease. Our study first described the changes in the composition of oral microorganisms and their metabolites in T2DM who have not suffered any oral diseases and revealed the correlation between oral microorganisms and their metabolites, which will provide a direct basis for finding oral biomarkers for early warning of oral diseases in patients with T2DM.
Keywords: metabolomic; metagenomic; oral diseases; oral microbiome; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, Malanda B, Karuranga S, Unwin N, Colagiuri S, Guariguata L, Motala AA, Ogurtsova K, Shaw JE, Bright D, Williams R, IDF Diabetes Atlas Committee . 2019. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 157:107843. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Laouali N, El Fatouhi D, Aguayo G, Balkau B, Boutron-Ruault M-C, Bonnet F, Fagherazzi G. 2021. Type 2 diabetes and its characteristics are associated with poor oral health: findings from 60,590 senior women from the E3N study. BMC Oral Health 21:315. doi: 10.1186/s12903-021-01679-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

