Surveillance Imaging after Primary Diagnosis of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
- PMID: 36625746
- PMCID: PMC10068891
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.221210
Surveillance Imaging after Primary Diagnosis of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ
Abstract
Background Guidelines recommend annual surveillance imaging after diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). Guideline adherence has not been characterized in a contemporary cohort. Purpose To identify uptake and determinants of surveillance imaging in women who underwent treatment for DCIS. Materials and Methods A stratified random sample of women who underwent breast-conserving surgery for primary DCIS between 2008 and 2014 was retrospectively selected from 1330 facilities in the United States. Imaging examinations were recorded from date of diagnosis until first distant recurrence, death, loss to follow-up, or end of study (November 2018). Imaging after treatment was categorized into 10 12-month periods starting 6 months after diagnosis. Primary outcome was per-period receipt of asymptomatic surveillance imaging (mammography, MRI, or US). Secondary outcome was diagnosis of ipsilateral invasive breast cancer. Multivariable logistic regression with repeated measures and generalized estimating equations was used to model receipt of imaging. Rates of diagnosis with ipsilateral invasive breast cancer were compared between women who did and those who did not undergo imaging in the 6-18-month period after diagnosis using inverse probability-weighted Kaplan-Meier estimators. Results A total of 12 559 women (median age, 60 years; IQR, 52-69 years) were evaluated. Uptake of surveillance imaging was 75% in the first period and decreased over time (P < .001). Across the first 5 years after treatment, 52% of women participated in consistent annual surveillance. Surveillance was lower in Black (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 0.80; 95% CI: 0.74, 0.88; P < .001) and Hispanic (OR, 0.82; 95% CI: 0.72, 0.94; P = .004) women than in White women. Women who underwent surveillance in the first period had a higher 6-year rate of diagnosis of invasive cancer (1.6%; 95% CI: 1.3, 1.9) than those who did not (1.1%; 95% CI: 0.7, 1.4; difference: 0.5%; 95% CI: 0.1, 1.0; P = .03). Conclusion Half of women did not consistently adhere to imaging surveillance guidelines across the first 5 years after treatment, with racial disparities in adherence rates. © RSNA, 2023 Supplemental material is available for this article. See also the editorial by Rahbar and Dontchos in this issue.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




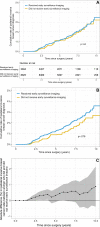
Comment in
-
Disparities in Imaging Surveillance after a DCIS Diagnosis Elucidate Persistent Inequities in the Breast Cancer Care Continuum.Radiology. 2023 Apr;307(1):e222900. doi: 10.1148/radiol.222900. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Radiology. 2023. PMID: 36625752 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Imaging Surveillance Programs: An Accessible Path to the Future.Radiology. 2023 Jun;307(5):e230250. doi: 10.1148/radiol.230250. Radiology. 2023. PMID: 37338361 No abstract available.
References
-
- Erbas B , Provenzano E , Armes J , Gertig D . The natural history of ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: a review . Breast Cancer Res Treat 2006. ; 97 ( 2 ): 135 – 144 . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

