Hypercapnia alters stroma-derived Wnt production to limit β-catenin signaling and proliferation in AT2 cells
- PMID: 36626234
- PMCID: PMC9977495
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.159331
Hypercapnia alters stroma-derived Wnt production to limit β-catenin signaling and proliferation in AT2 cells
Abstract
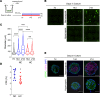
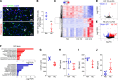
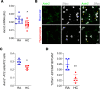
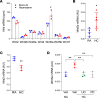
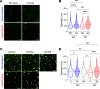
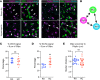
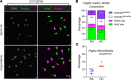
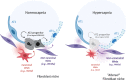
Persistent symptoms and radiographic abnormalities suggestive of failed lung repair are among the most common symptoms in patients with COVID-19 after hospital discharge. In mechanically ventilated patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) secondary to SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, low tidal volumes to reduce ventilator-induced lung injury necessarily elevate blood CO2 levels, often leading to hypercapnia. The role of hypercapnia on lung repair after injury is not completely understood. Here - using a mouse model of hypercapnia exposure, cell lineage tracing, spatial transcriptomics, and 3D cultures - we show that hypercapnia limits β-catenin signaling in alveolar type II (AT2) cells, leading to their reduced proliferative capacity. Hypercapnia alters expression of major Wnts in PDGFRα+ fibroblasts from those maintaining AT2 progenitor activity toward those that antagonize β-catenin signaling, thereby limiting progenitor function. Constitutive activation of β-catenin signaling in AT2 cells or treatment of organoid cultures with recombinant WNT3A protein bypasses the inhibitory effects of hypercapnia. Inhibition of AT2 proliferation in patients with hypercapnia may contribute to impaired lung repair after injury, preventing sealing of the epithelial barrier and increasing lung flooding, ventilator dependency, and mortality.
Keywords: Cell Biology; Pulmonology; Respiration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Coronovirus Resource Center. Johns Hopkins University & Medicine. Updated February 9, 2023. Accessed Febcurary 9, 2023. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I01 CX001777/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 HL163611/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL154998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM129312/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147575/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134800/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL076139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG075423/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147070/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL158139/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

