Dietary essential amino acids for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
- PMID: 36626303
- PMCID: PMC10153641
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvad005
Dietary essential amino acids for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
Abstract
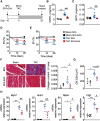
Aims: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is a leading cause of mortality worldwide, requiring novel therapeutic and lifestyle interventions. Metabolic alterations and energy production deficit are hallmarks and thereby promising therapeutic targets for this complex clinical syndrome. We aim to study the molecular mechanisms and effects on cardiac function in rodents with HFrEF of a designer diet in which free essential amino acids-in specifically designed percentages-substituted for protein.
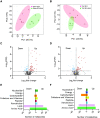
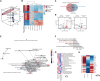
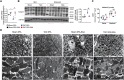
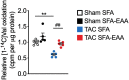
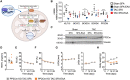
Methods and results: Wild-type mice were subjected to transverse aortic constriction (TAC) to induce left ventricle (LV) pressure overload or sham surgery. Whole-body glucose homeostasis was studied with glucose tolerance test, while myocardial dysfunction and fibrosis were measured with echocardiogram and histological analysis. Mitochondrial bioenergetics and morphology were investigated with oxygen consumption rate measurement and electron microscopy evaluation. Circulating and cardiac non-targeted metabolite profiles were analyzed by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectroscopy, while RNA-sequencing was used to identify signalling pathways mainly affected. The amino acid-substituted diet shows remarkable preventive and therapeutic effects. This dietary approach corrects the whole-body glucose metabolism and restores the unbalanced metabolic substrate usage-by improving mitochondrial fuel oxidation-in the failing heart. In particular, biochemical, molecular, and genetic approaches suggest that renormalization of branched-chain amino acid oxidation in cardiac tissue, which is suppressed in HFrEF, plays a relevant role. Beyond the changes of systemic metabolism, cell-autonomous processes may explain at least in part the diet's cardioprotective impact.
Conclusion: Collectively, these results suggest that manipulation of dietary amino acids, and especially essential amino acids, is a potential adjuvant therapeutic strategy to treat systolic dysfunction and HFrEF in humans.
Keywords: Amino acids; Heart failure; Mitochondrial function; Nutrition; Transcriptomic reprogramming.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Das SR, Delling FN, Djousse L, Elkind MSV, Ferguson JF, Fornage M, Jordan LC, Khan SS, Kissela BM, Knutson KL, Kwan TW, Lackland DT, Lewis TT, Lichtman JH, Longenecker CT, Loop MS, Lutsey PL, Martin SS, Matsushita K, Moran AE, Mussolino ME, O’Flaherty M, Pandey A, Perak AM, Rosamond WD, Roth GA, Sampson UKA, Satou GM, Schroeder EB, Shah SH, Spartano NL, Stokes A, Tirschwell DL, Tsao CW, Turakhia MP, VanWagner LB, Wilkins JT, Wong SS, Virani SS. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American heart association. Circulation 2019;139:e56–e528. - PubMed
-
- Rossignol P, Hernandez AF, Solomon SD, Zannad F. Heart failure drug treatment. Lancet. 2019;393:1034–1044. - PubMed
-
- Gheorghiade M, Larson CJ, Shah SJ, Greene SJ, Cleland JGF, Colucci WS, Dunnmon P, Epstein SE, Kim RJ, Parsey RV, Stockbridge N, Carr J, Dinh W, Krahn T, Kramer F, Wahlander K, Deckelbaum LI, Crandall D, Okada S, Senni M, Sikora S, Sabbah HN, Butler J. Developing new treatments for heart failure: Focus on the Heart. Circ Hear Fail 2016;9:e002727. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

