A novel prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma based on cuproptosis-related lncRNAs: A Review
- PMID: 36626411
- PMCID: PMC9750635
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031924
A novel prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma based on cuproptosis-related lncRNAs: A Review
Abstract
Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) is a highly heterogeneous disease with complex pathogenesis, high mortality, and poor prognosis. Cuproptosis is a new type of programmed cell death triggered by copper accumulation that may play an important role in cancer. LncRNAs are becoming valuable prognostic factors in cancer patients. The effect of cuproptosis-related lncRNAs (CRlncRNAs) on LUAD has not been clarified. Based on the Cancer Genome Atlas database, CRlncRNAs were screened by co-expression analysis of cuproptosis- related genes and lncRNAs. Using CRlncRNAs, Cox and LASSO regression analyses constructed a risk prognostic model. The predictive efficacy of the model was assessed and validated using survival analysis, receiver operating characteristic curve, univariate and multifactor Cox regression analysis, and principal component analysis. A nomogram was constructed and calibration curves were applied to enhance the predictive efficacy of the model. Tumor Mutational Burden analysis and chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity prediction were performed to assess the clinical feasibility of the risk model. The novel prognostic signature consisted of 5 potentially high-risk CRlncRNAs, MAP3K20-AS1, CRIM1-DT, AC006213.3, AC008035.1, and NR2F2-AS1, and 5 potentially protective CRlncRNAs, AC090948.1, AL356481.1, AC011477.2, AL031600.2, and AC026355.2, which had accurate and robust predictive power for LUAD patients. Collectively, the novel prognostic signature constructed based on CRlncRNAs can effectively assess and predict the prognosis of patients and provide a new perspective for the diagnosis and treatment of LUAD.
Copyright © 2022 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
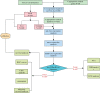
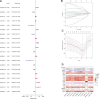
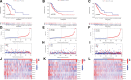
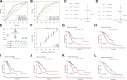


Similar articles
-
Establishment of a prognostic signature for lung adenocarcinoma using cuproptosis-related lncRNAs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Mar 6;24(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05192-5. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36879187 Free PMC article.
-
A cuproptosis-related lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis and immunotherapy response of lung adenocarcinoma.Hereditas. 2023 Jul 24;160(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s41065-023-00293-w. Hereditas. 2023. PMID: 37482612 Free PMC article.
-
Cuproptosis-related lncRNA predict prognosis and immune response of lung adenocarcinoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2022 Sep 1;20(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12957-022-02727-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36050740 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a cuproptosis-related lncRNA prognostic signature in lung adenocarcinoma.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Jun;25(6):1617-1628. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-03057-6. Epub 2023 Jan 7. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36609650
-
A cuproptosis-related long non-coding RNA signature to predict the prognosis and immune microenvironment characterization for lung adenocarcinoma.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022 Oct;11(10):2079-2093. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-22-660. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36386454 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advancing lung adenocarcinoma prognosis and immunotherapy prediction with a multi-omics consensus machine learning approach.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jul;28(13):e18520. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18520. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38958523 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and Prognosis of Biological Microenvironment in Lung Adenocarcinoma through a Disulfidptosis-Related lncRNAs Signature.Genet Res (Camb). 2023 Aug 4;2023:6670514. doi: 10.1155/2023/6670514. eCollection 2023. Genet Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37575978 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of cuproptosis and disulfidptosis-related lncRNA in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma prognosis and treatment.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 17;10(18):e37996. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37996. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39323825 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis-related LncRNAs in diseases.BMC Biol. 2025 Jun 6;23(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12915-025-02268-x. BMC Biol. 2025. PMID: 40481573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CBFA2T3 as a Key Prognostic Biomarker in Lung Adenocarcinoma: Insights from Comprehensive Analysis and Validation.Biochem Genet. 2025 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s10528-025-11224-x. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 40804206
References
-
- Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV, et al. . Lung cancer. Lancet. 2021;398:535–54. - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, et al. . Introduction to The 2015 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the lung, pleura, thymus, and heart. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10:1240–2. - PubMed
-
- Rinn JL, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs: molecular modalities to organismal functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 2020;89:283–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

