Dual-specificity RNA aptamers enable manipulation of target-specific O-GlcNAcylation and unveil functions of O-GlcNAc on β-catenin
- PMID: 36626902
- PMCID: PMC9868088
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.12.016
Dual-specificity RNA aptamers enable manipulation of target-specific O-GlcNAcylation and unveil functions of O-GlcNAc on β-catenin
Abstract
O-GlcNAc is a dynamic post-translational modification (PTM) that regulates protein functions. In studying the regulatory roles of O-GlcNAc, a major roadblock is the inability to change O-GlcNAcylation on a single protein at a time. Herein, we developed a dual RNA-aptamer-based approach that simultaneously targeted O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and β-catenin, the key transcription factor of the Wnt signaling pathway, to selectively increase O-GlcNAcylation of the latter without affecting other OGT substrates. Using the OGT/β-catenin dual-specificity aptamers, we found that O-GlcNAcylation of β-catenin stabilizes the protein by inhibiting its interaction with β-TrCP. O-GlcNAc also increases β-catenin's interaction with EZH2, recruits EZH2 to promoters, and dramatically alters the transcriptome. Further, by coupling riboswitches or an inducible expression system to aptamers, we enabled inducible regulation of protein-specific O-GlcNAcylation. Together, our findings demonstrate the efficacy and versatility of dual-specificity aptamers for regulating O-GlcNAcylation on individual proteins.
Keywords: EZH2; O-GlcNAc; O-GlcNAc transferase; RNA; Wnt signaling; aptamer; post-translational modification; riboswitch; transcriptome; β-catenin.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests A patent application based on this work has been filed. G.W.H. and Y.Z. are inventors of this patent.
Figures

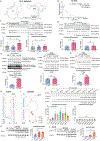
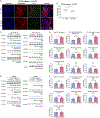
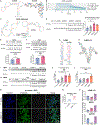
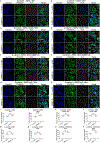


Comment in
-
Dual-specificity RNA aptamers: A sweet new tool for studying O-GlcNAc biology.Mol Cell. 2023 Mar 2;83(5):657-659. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.01.025. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 36868188
References
-
- Torres CR, and Hart GW (1984). Topography and polypeptide distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine residues on the surfaces of intact lymphocytes. Evidence for O-linked GlcNAc. J Biol Chem 259, 3308–3317. - PubMed
-
- Hanover JA, Cohen CK, Willingham MC, and Park MK (1987). O-linked N-acetylglucosamine is attached to proteins of the nuclear pore. Evidence for cytoplasmic and nucleoplasmic glycoproteins. J Biol Chem 262, 9887–9894. - PubMed
-
- Haltiwanger RS, Blomberg MA, and Hart GW (1992). Glycosylation of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins. Purification and characterization of a uridine diphospho-N-acetylglucosamine:polypeptide beta-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. J Biol Chem 267, 9005–9013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

