Disruption of Ovarian Cancer STAT3 and p38 Signaling with a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of PTP4A3 Phosphatase
- PMID: 36627205
- PMCID: PMC9976793
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.122.001401
Disruption of Ovarian Cancer STAT3 and p38 Signaling with a Small-Molecule Inhibitor of PTP4A3 Phosphatase
Abstract
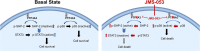
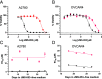
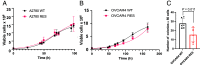
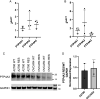
Protein tyrosine phosphatase type IVA member 3 (PTP4A3 or PRL-3) is a nonreceptor, oncogenic, dual-specificity phosphatase that is highly expressed in many human tumors, including ovarian cancer, and is associated with a poor patient prognosis. Recent studies suggest that PTP4A3 directly dephosphorylates SHP-2 phosphatase as part of a STAT3-PTP4A3 feedforward loop and directly dephosphorylates p38 kinase. The goal of the current study was to examine the effect of a PTP4A phosphatase inhibitor, 7-imino-2-phenylthieno[3,2-c]pyridine-4,6(5H,7H)-dione (JMS-053), on ovarian cancer STAT3, SHP-2, and p38 kinase phosphorylation. JMS-053 caused a concentration- and time-dependent decrease in the activated form of STAT3, Y705 phospho-STAT3, in ovarian cancer cells treated in vitro. In contrast, the phosphorylation status of two previously described direct PTP4A3 substrates, SHP-2 phosphatase and p38 kinase, were rapidly increased with JMS-053 treatment. We generated A2780 and OVCAR4 ovarian cancer cells resistant to JMS-053, and the resulting cells were not crossresistant to paclitaxel, cisplatin, or teniposide. JMS-053-resistant A2780 and OVCAR4 cells exhibited a 95% and 50% decrease in basal Y705 phospho-STAT3, respectively. JMS-053-resistant OVCAR4 cells had an attenuated phosphorylation and migratory response to acute exposure to JMS-053. These results support a regulatory role for PTP4A phosphatase in ovarian cancer cell STAT3 and p38 signaling circuits. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: This study demonstrates that chemical inhibition of PTP4A phosphatase activity with JMS-053 decreases STAT3 activation and increases SHP-2 phosphatase and p38 kinase phosphorylation activation in ovarian cancer cells. The newly developed JMS-053-resistant ovarian cancer cells should provide useful tools to further probe the role of PTP4A phosphatase in ovarian cancer cell survival and cell signaling.
Copyright © 2023 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures





References
-
- Aguilar-Sopeña O, Hernández-Pérez S, Alegre-Gómez S, Castro-Sánchez P, Iglesias-Ceacero A, Lazo JS, Roda-Navarro P (2020) Effect of Pharmacological Inhibition of the Catalytic Activity of Phosphatases of Regenerating Liver in Early T Cell Receptor Signaling Dynamics and IL-2 Production. Int J Mol Sci 21:2530. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Behrens BC, Hamilton TC, Masuda H, Grotzinger KR, Whang-Peng J, Louie KG, Knutsen T, McKoy WM, Young RC, Ozols RF (1987) Characterization of a cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-resistant human ovarian cancer cell line and its use in evaluation of platinum analogues. Cancer Res 47:414–418. - PubMed
-
- Chong PSYZhou JLim JSLHee YTChooi JYChung THTan ZTZeng QWaller DDSebag M, et al. (2019) IL6 promotes a STAT3-PRL3 feedforward loop via SHP2 repression in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res 79:4679–4688. - PubMed
-
- Cowley GSWeir BAVazquez FTamayo PScott JARusin SEast-Seletsky AAli LDGerath WFPantel SE, et al. (2014) Parallel genome-scale loss of function screens in 216 cancer cell lines for the identification of context-specific genetic dependencies [published correction appears in Sci Data (2014) 1:140044]. Sci Data 1:140035. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gottesman MM (2002) Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu Rev Med 53:615–627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

