Inequalities in children's mental health care: analysis of routinely collected data on prescribing and referrals to secondary care
- PMID: 36627578
- PMCID: PMC9831880
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-022-04438-5
Inequalities in children's mental health care: analysis of routinely collected data on prescribing and referrals to secondary care
Abstract
Background: One in eight children in the United Kingdom are estimated to have a mental health condition, and many do not receive support or treatment. The COVID-19 pandemic has negatively impacted mental health and disrupted the delivery of care. Prevalence of poor mental health is not evenly distributed across age groups, by sex or socioeconomic groups. Equity in access to mental health care is a policy priority but detailed socio-demographic trends are relatively under-researched.
Methods: We analysed records for all mental health prescriptions and referrals to specialist mental health outpatient care between the years of 2015 and 2021 for children aged 2 to 17 years in a single NHS Scotland health board region. We analysed trends in prescribing, referrals, and acceptance to out-patient treatment over time, and measured differences in treatment and service use rates by age, sex, and area deprivation.
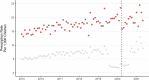
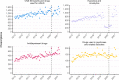
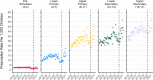
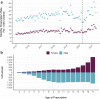
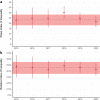
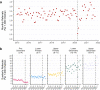
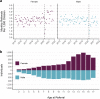
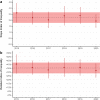
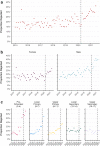
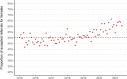
Results: We identified 18,732 children with 178,657 mental health prescriptions and 21,874 referrals to specialist outpatient care. Prescriptions increased by 59% over the study period. Boys received double the prescriptions of girls and the rate of prescribing in the most deprived areas was double that in the least deprived. Mean age at first mental health prescription was almost 1 year younger in the most deprived areas than in the least. Referrals increased 9% overall. Initially, boys and girls both had an annual referral rate of 2.7 per 1000, but this fell 6% for boys and rose 25% for girls. Referral rate for the youngest decreased 67% but increased 21% for the oldest. The proportion of rejected referrals increased steeply since 2020 from 17 to 30%. The proportion of accepted referrals that were for girls rose to 62% and the mean age increased 1.5 years.
Conclusions: The large increase in mental health prescribing and changes in referrals to specialist outpatient care aligns with emerging evidence of increasing poor mental health, particularly since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. The static size of the population accepted for specialist treatment amid greater demand, and the changing demographics of those accepted, indicate clinical prioritisation and unmet need. Persistent inequities in mental health prescribing and referrals require urgent action.
Keywords: CAMHS; Child & adolescent mental health; Health inequalities; Mental health prescribing.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sadler K, Vizard T, Ford T, Marcheselli F, Pearce N, Mandalia D, et al. Mental health of children and young people in England, 2017: summary of key findings. NHS Digital. 2018; Available from: https://files.digital.nhs.uk/A6/EA7D58/MHCYP%202017%20Summary.pdf [cited 31 Jan 2022].
-
- Radez J, Reardon T, Creswell C, Lawrence PJ, Evdoka-Burton G, Waite P. Why do children and adolescents (not) seek and access professional help for their mental health problems? A systematic review of quantitative and qualitative studies. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021;30(2):183–211. doi: 10.1007/s00787-019-01469-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Radez J, Reardon T, Creswell C, Orchard F, Waite P. Adolescents’ perceived barriers and facilitators to seeking and accessing professional help for anxiety and depressive disorders: a qualitative interview study. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021; Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00787-020-01707-0 [cited 17 Dec 2021]. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gould N. Mental health and child poverty. York: Joseph Rowntree Foundation; 2006.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

