Determinants of breast self-examination practice among women attending pastoralist health facilities, Southern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 36627644
- PMCID: PMC9832667
- DOI: 10.1186/s12905-023-02158-w
Determinants of breast self-examination practice among women attending pastoralist health facilities, Southern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer remains the most serious public health problem affecting millions of women worldwide. Despite various studies regarding breast self-examination practices conducted among health professionals and students in Ethiopia, limited information was found on women attending health care services in the pastoralist community. This study aimed to identify the determinants of breast self-examination practice (BSE) among women attending pastoralist health facilities in Southern Ethiopia.
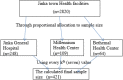
Methods: An institutional-based cross-sectional study was conducted among 421 women who were attending family planning services in pastoralist health facilities in South Omo Zone, Southern Ethiopia from January to February 2022 using systematic random sampling to select a woman from each health facility in Jinka town. Data were collected using structured, pretested, and interviewer-administered questionnaires. Descriptive statistics such as proportions, means, and standard deviations were used to describe each relevant variable. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify the determinants of BSE practices among women.
Result: The mean age of the women was 25.43 ± 6.66 years. Fifty-four percent (n = 173) of the women had heard of BSE from health professionals. Eighty-nine (21.1%) women had undergone BSE. Women who resided in the urban areas (AOR = 6.79, CI: 3.40, 13.56), attained at least primary education and above (AOR = 8.96, CI: 4.14, 19.35), heard about BSE (AOR = 4.07, CI: 2.07, 7.98), and had a family history of breast cancer (AOR = 7.46, CI = 3.27, 17.00) were significantly associated with BSE practice.
Conclusion and recommendation: Our study showed that women's practice of BSE was lower when compared with the local studies. We recommend health care professionals and others working in the area improve ways of increasing awareness about breast cancer, including its risk, and the need for BSE.
Keywords: Breast self-examination; Breast self-examination practices; Pastoralists; Southern Ethiopia.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no potential competing interests exist.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

