Development of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgG and IgA antibodies in serum and milk with different SARS-COV-2 vaccines in lactating women
- PMID: 36627706
- PMCID: PMC9831888
- DOI: 10.1186/s13006-022-00536-y
Development of SARS-CoV-2 specific IgG and IgA antibodies in serum and milk with different SARS-COV-2 vaccines in lactating women
Abstract
Background: Our main objective was to determine the evolution of IgG and IgA antibodies directed against SARS-CoV-2 protein S in the blood of lactating women and in breast milk.
Methods: A cohort of 110 uninfected and vaccinated breastfeeding women was followed-up for 6 months at the Marqués de Valdecilla University Hospital, Spain, in 2020. An additional group of 23 breastfeeding mothers who had no previously documented infection and had not been vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 were included as a control group. The antibodies in blood and breast milk and their evolution at 6 months post-vaccination were analysed.
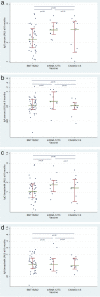
Results: One hundred ten breastfeeding mothers were included; 70 women (63.6%) were vaccinated with two doses of BNT162b2, 20 women (18.2%) received two doses of mRNA-1273, and 20 women (18.2%) received a single dose of ChAdOx1-S. No evidence of differences between concentrations of antibodies was found according to the type of vaccine, with the exception of serum IgA antibodies, which was higher in women vaccinated with mRNA-1273: mean [95%CI]: 0.05 AU/mL [0.03,0.06] with mRNA-1273, 0.02 AU/mL [0.01,0.03] with BNT162b2 and 0.01 AU/mL [0.00,0.03] with ChAdOx1-S, ANOVA p value = 0.03. The lack of difference between vaccines was also found when anti-S1 specific IgG in serum and breast milk were measured.
Conclusions: In lactating women vaccinated against COVID-19, anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies can be detected in both serum and breastmilk 6 months after receiving the second dose, although their concentrations decreased when compared with concentrations reached immediately after vaccination.
Keywords: Adverse effects; Antibodies; Breast milk; Breastfeeding; Maternal immunity; Neonatal immunity; SARS-COV-2 vaccine.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- American Academy of Family Physicians. Breastfeeding, Family Physicians Supporting (Position Paper). Available at: https://www.aafp.org/about/policies/all/breastfeeding-support.html (Accessed on 02 Jul 2019).
-
- World Health Organization. Breastfeeding. Available at: https://www.who.int/topics/breastfeeding/en/ (Accessed on 02 Jul 2019).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous