Drug and apoptosis resistance in cancer stem cells: a puzzle with many pieces
- PMID: 36627897
- PMCID: PMC9771762
- DOI: 10.20517/cdr.2022.20
Drug and apoptosis resistance in cancer stem cells: a puzzle with many pieces
Abstract
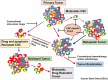
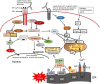
Resistance to anticancer agents and apoptosis results in cancer relapse and is associated with cancer mortality. Substantial data have provided convincing evidence establishing that human cancers emerge from cancer stem cells (CSCs), which display self-renewal and are resistant to anticancer drugs, radiation, and apoptosis, and express enhanced epithelial to mesenchymal progression. CSCs represent a heterogeneous tumor cell population and lack specific cellular targets, which makes it a great challenge to target and eradicate them. Similarly, their close relationship with the tumor microenvironment creates greater complexity in developing novel treatment strategies targeting CSCs. Several mechanisms participate in the drug and apoptosis resistance phenotype in CSCs in various cancers. These include enhanced expression of ATP-binding cassette membrane transporters, activation of various cytoprotective and survival signaling pathways, dysregulation of stemness signaling pathways, aberrant DNA repair mechanisms, increased quiescence, autophagy, increased immune evasion, deficiency of mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis, upregulation of anti-apoptotic proteins including c-FLIP [cellular FLICE (FADD-like IL-1β-converting enzyme)-inhibitory protein], Bcl-2 family members, inhibitors of apoptosis proteins, and PI3K/AKT signaling. Studying such mechanisms not only provides mechanistic insights into these cells that are unresponsive to drugs, but may lead to the development of targeted and effective therapeutics to eradicate CSCs. Several studies have identified promising strategies to target CSCs. These emerging strategies may help target CSC-associated drug resistance and metastasis in clinical settings. This article will review the CSCs drug and apoptosis resistance mechanisms and how to target CSCs.
Keywords: Bcl-2 family; Cancer stem cells (CSCs); anti-apoptotic proteins; apoptosis; c-FLIP; death receptor pathways; drug resistance.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Resistance to drugs and cell death in cancer stem cells (CSCs).J Transl Sci. 2020 Jun;6(3):341. doi: 10.15761/jts.1000341. Epub 2019 Jun 24. J Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 35330670 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Therapeutic Targeting of Cancer Stem Cells within the Tumor Microenvironment: An Updated Review.Cells. 2020 Aug 13;9(8):1896. doi: 10.3390/cells9081896. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32823711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resistance to Cell Death and Its Modulation in Cancer Stem Cells.Crit Rev Oncog. 2016;21(3-4):203-219. doi: 10.1615/CritRevOncog.2016016976. Crit Rev Oncog. 2016. PMID: 27915972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stem cell programs in cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 9;10(19):8721-8743. doi: 10.7150/thno.41648. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32754274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoprotective effect of neuropeptides on cancer stem cells: vasoactive intestinal peptide-induced antiapoptotic signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Jun 1;8(6):e2844. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.226. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28569785 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Supramolecular host-guest nanosystems for overcoming cancer drug resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2023 Nov 22;6(4):805-827. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2023.77. eCollection 2023. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 38263983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer cell cycle heterogeneity as a critical determinant of therapeutic resistance.Genes Dis. 2023 Jan 14;11(1):189-204. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2022.11.025. eCollection 2024 Jan. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 37588236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diethyldithiocarbamate-ferrous oxide nanoparticles inhibit human and mouse glioblastoma stemness: aldehyde dehydrogenase 1A1 suppression and ferroptosis induction.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;15:1363511. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1363511. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38720782 Free PMC article.
-
Ellagic Acid Induces DNA Damage and Apoptosis in Cancer Stem-like Cells and Overcomes Cisplatin Resistance.ACS Omega. 2024 Dec 5;9(50):48988-49000. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08819. eCollection 2024 Dec 17. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39713677 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium electroporation induces stress response through upregulation of HSP27, HSP70, aspartate β-hydroxylase, and CD133 in human colon cancer cells.Biol Res. 2025 Feb 21;58(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40659-025-00591-9. Biol Res. 2025. PMID: 39980072 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
