Budget impact analysis sull’introduzione del dispositivo di telemonitoraggio Turbo+ nella gestione dei pazienti asmatici in Italia
- PMID: 36628312
- PMCID: PMC9768613
- DOI: 10.33393/grhta.2022.2290
Budget impact analysis sull’introduzione del dispositivo di telemonitoraggio Turbo+ nella gestione dei pazienti asmatici in Italia
Abstract
Introduction:: Adherence to long-term asthma control drugs is one of the key factors in improving disease management among patients with asthma. Poor adherence to long-term therapies significantly compromises the effectiveness of treatment and represents a problem in controlling the disease in terms of quality of life and economic impact. A budget impact analysis has been developed taking into account that Turbo+ technology (electronic monitoring device) can increase adherence to therapy in patients suffering from asthma.
Methods:: Coherently with the budget impact model methodology, we developed two different scenarios. One represents the clinical practice assuming a constant market share of 0,99% for Turbo+ and the other one assumes an incremental market share of Turbo+ over the time horizon considered. An increase in adherence to therapy will likely correspond to a reduction of exacerbations and a lower rate of hospitalizations, thus generating savings in terms of use of health resources.
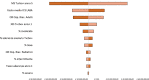
Results:: The differential analysis shows an incremental saving in terms of resources absorbed by the National Health Service (NHS) over the time horizon considered. In the first year the savings are equal to € 795,658.64 and in the fifth year they are equal to € 3,520,636.34 for a total of resources saved in 5 years of € 10,882,028.50.
Conclusions:: The model shows how the diffusion of the Turbo+ programme can lead to savings in terms of health resources consumed by the NHS. Further analyses with new real-world data on adherence in asthmatic patients could be useful in confirming the results of the present analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Global Asthma Network. The Global Asthma Report 2018. [Accessed June; 2021 ]; Online
-
- Vos T, Lim SS, Abbafati C et al. GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. 2020;396(10258):1204–1222. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30925-9. PubMed - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brian C. 2nd. CRC Press; 2011. Leutholtz, Ignacio Ripoll, Exercise and disease management, p. 100.
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) – Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention; [Accessed May; 2021 ]; Online
-
- Johansson G, Andreasson EB, Larsson PE, Vogelmeier CF. Cost effectiveness of budesonide/formoterol for maintenance and reliever therapy versus salmeterol/fluticasone plus salbutamol in the treatment of asthma. Pharmacoeconomics. 2006;24(7):695–708. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200624070-00008. PubMed - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources