Modulation of Inula racemosa Hook Extract on Cardioprotection by Ischemic Preconditioning in Hyperlipidaemic Rats
- PMID: 36628345
- PMCID: PMC9806160
- DOI: 10.3831/KPI.2022.25.4.369
Modulation of Inula racemosa Hook Extract on Cardioprotection by Ischemic Preconditioning in Hyperlipidaemic Rats
Abstract
Objectives: Hyperlipidemia (HL) is a major cause of ischemic heart diseases. The size-limiting effect of ischemic preconditioning (IPC), a cardioprotective phenomenon, is reduced in HL, possibly because of the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP). The objective of this study is to see what effect pretreatment with Inula racemosa Hook root extract (IrA) had on IPC-mediated cardioprotection on HL Wistar rat hearts. An isolated rat heart was mounted on the Langendorff heart array, and then ischemia reperfusion (I/R) and IPC cycles were performed. Atractyloside (Atr) is an MPTP opener.
Methods: The animals were divided into ten groups, each consisting of six rats (n = 6), to investigate the modulation of I. racemosa Hook extract on cardioprotection by IPC in HL hearts Sham control, I/R Control, IPC control, I/R + HL, I/R + IrA + HL, IPC + HL, IPC + NS + HL, IPC + IrA+ HL, IPC + Atr + oxidative stress, mitochondrial function, integrity, and hemodynamic parameters are evaluated for each group.
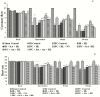
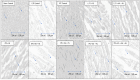
Results: The present experimental data show that pretreatment with IrA reduced the LDH, CK-MB, size of myocardial infarction, content of cardiac collagen, and ventricular fibrillation in all groups of HL rat hearts. This pretreatment also reduced the oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Inhibition of MPTP opening by Atr diminished the effect of IrA on IPC-mediated cardioprotection in HL rats.
Conclusion: The study findings indicate that pretreatment with IrA e restores IPC-mediated cardioprotection in HL rats by inhibiting the MPTP opening.
Keywords: hyperlipidaemia; ischemic preconditioning; mitochondria; oxidative stress.
© 2022 Korean Pharmacopuncture Institute.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Wang Y, Wang Y, Li S, Cui Y, Liang X, Shan J, et al. Functionalized nanoparticles with monocyte membranes and rapamycin achieve synergistic chemoimmunotherapy for reperfusion-induced injury in ischemic stroke. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021;19(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-01067-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
