Crystal structures of (Z)-(ethene-1,2-di-yl)bis-(di-phenyl-phosphine sulfide) and its complex with PtII dichloride
- PMID: 36628368
- PMCID: PMC9815131
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022011847
Crystal structures of (Z)-(ethene-1,2-di-yl)bis-(di-phenyl-phosphine sulfide) and its complex with PtII dichloride
Abstract
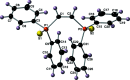
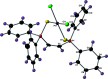
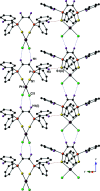
The crystal structures of (Z)-(ethene-1,2-di-yl)bis-(di-phenyl-phosphine sulfide), C26H22P2S2 (I), along with its complex with PtII dichloride, di-chlorido[(Z)-(ethene-1,2-di-yl)bis-(di-phenyl-phosphine sulfide)-κ2 S,S']platinum(II), [PtCl2(C26H22P2S2)] (II), are described here. Compound I features P=S bond lengths of 1.9571 (15) and 1.9529 (15) Å, with a torsion angle of 166.24 (7)° between the two phosphine sulfide groups. The crystal of compound I features both intra-molecular C-H⋯S hydrogen bonds and π-π inter-actions. Mol-ecules of compound I are held together with inter-molecular π-π and C-H⋯π inter-actions to form chains that run parallel to the z-axis. The inter-molecular C-H⋯π inter-action has a H⋯Cg distance of 2.63 Å, a D⋯Cg distance of 3.573 (5) Å and a D-H⋯Cg angle of 171° (where Cg refers to the centroid of one of the phenyl rings). These chains are linked by relatively long C-H⋯S hydrogen bonds with D⋯A distances of 3.367 (4) and 3.394 (4) Å with D-H⋯A angles of 113 and 115°. Compound II features Pt-Cl and Pt-S bond lengths of 2.3226 (19) and 2.2712 (19) Å, with a P=S bond length of 2.012 (3) Å. The PtII center adopts a square-planar geometry, with Cl-Pt-Cl and S-Pt-S bond angles of 90.34 (10) and 97.19 (10)°, respectively. Mol-ecules of compound II are linked in the crystal by inter-molecular C-H⋯Cl and C-H⋯S hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: C—H⋯Cl hydrogen bond; C—H⋯S hydrogen bond; C—H⋯π interaction; PtII complex; crystal structure; phosphine sulfide; π–π interaction.
© Rawls et al. 2023.
Figures









References
-
- Aguiar, A. M. & Daigle, D. (1964). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86, 5354–5355.
-
- Aullón, G., Bellamy, D., Orpen, A.G., Brammer, L. & Bruton, E. A. (1998). Chem. Commun. pp. 653–654.
-
- Banda, S. F. & Pritchard, R. G. (2008). Orient. J. Chem. 24, 17–22.
-
- Bernabé-Pablo, E., Campirán-Martínez, A., Jancik, V., Martínez-Otero, D. & Moya-Cabrera, M. (2016). Polyhedron, 110, 305–313.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
