Validation of the North America expert consensus statement on reporting CT findings for COVID-19 in individuals with lung cancer
- PMID: 36629525
- PMCID: PMC9828872
- DOI: 10.1590/1414-431X2022e12376
Validation of the North America expert consensus statement on reporting CT findings for COVID-19 in individuals with lung cancer
Abstract
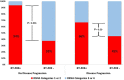
The aim of our study was to validate the use of the standardized Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) reporting system in individuals with known lung cancer who presented to the emergency department with suspected COVID-19. We included patients aged 18 years or older from the Cancer Institute of the State of São Paulo (ICESP) with a confirmed diagnosis of lung cancer, admitted to the emergency department and undergoing chest computed tomography (CT) for suspicion of COVID-19. Comparison between SARS-CoV2 RT-PCR across RSNA categories was performed in all patients and further stratified by diagnosis of lung cancer progression. Among 58 individuals included in the analysis (65±9 years, 43% men), 20 had positive RT-PCR. Less than a half (43%) had no new lung findings in the CT. Positive RT-PCR was present in 75% of those with typical findings according to RSNA and in only 9% when these findings were classified as atypical or negative (P<0.001). Diagnostic accuracy was even higher when stratified by the presence or absence of progressive disease (PD). Extent of pulmonary inflammatory changes was strongly associated with higher mortality, reaching a lethality of 83% in patients with >25% of lung involvement and 100% when there was >50% of lung involvement. The lung involvement score was also highly predictive of prognosis in this population as was reported for non-lung cancer individuals. Collectively, our results demonstrated that diagnostic and prognostic values of chest CT findings in COVID-19 are robust to the presence of lung abnormalities related to lung cancer.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) Expert Consensus Statement Related to Chest CT Findings in COVID-19 Versus CO-RADS: Comparison of Reporting System Performance Among Chest Radiologists and End-User Preference.Can Assoc Radiol J. 2021 Nov;72(4):806-813. doi: 10.1177/0846537120968919. Epub 2020 Nov 3. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2021. PMID: 33138634
-
RSNA Expert Consensus Statement on Reporting Chest CT Findings Related to COVID-19: Interobserver Agreement Between Chest Radiologists.Can Assoc Radiol J. 2021 Feb;72(1):159-166. doi: 10.1177/0846537120938328. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2021. PMID: 32615802 Free PMC article.
-
RSNA and BSTI grading systems of COVID-19 pneumonia: comparison of the diagnostic performance and interobserver agreement.BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Oct 4;21(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00668-3. BMC Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34602051 Free PMC article.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Mar 16;3:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub4. PMID: 33242342 Updated.
-
Thoracic imaging tests for the diagnosis of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 30;9:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Nov 26;11:CD013639. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013639.pub3. PMID: 32997361 Updated.
References
-
- Dai M, Liu D, Liu M, Zhou F, Li G, Chen Z, et al. Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2: a multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak. Cancer Discov. 2020;10:783–791. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0422. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

