Decoding Deep Learning applications for diagnosis and treatment planning
- PMID: 36629630
- PMCID: PMC9829109
- DOI: 10.1590/2177-6709.27.5.e22spe5
Decoding Deep Learning applications for diagnosis and treatment planning
Abstract
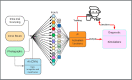
Introduction: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning and Deep Learning are playing an increasingly significant role in the medical field in the 21st century. These recent technologies are based on the concept of creating machines that have the potential to function as a human brain. It necessitates the gathering of large quantity of data to be processed. Once processed with AI machines, these data have the potential to streamline and improve the capabilities of the medical field in diagnosis and treatment planning, as well as in the prediction and recognition of diseases. These concepts are new to Orthodontics and are currently limited to image processing and pattern recognition.
Objective: This article exposes and describes the different methods by which orthodontics may benefit from a more widespread adoption of these technologies.
Introdução:: Inteligência Artificial (AI, de Artificial Intelligence), Machine Learning (Aprendizado de máquinas) e Deep Learning (Aprendizado Profundo) possuem um papel significativo e crescente na área médica do século 21. Essas tecnologias recentes são baseadas no conceito de criar máquinas com potencial de funcionar como um cérebro humano. Isso demanda que uma grande quantidade de dados seja reunida para ser processada. Uma vez processados em máquinas com AI, esses dados têm o potencial de agilizar e potencializar as capacidades de diagnóstico e planejamento do tratamento nas áreas médicas, assim como no diagnóstico e prognóstico de doenças. Esses são conceitos novos na Ortodontia, que atualmente são subutilizados, limitando-se ao processamento de imagens e reconhecimento de padrões.
Objetivo:: O presente artigo expõe e descreve os diferentes métodos pelos quais os ortodontistas podem se beneficiar com o uso mais abrangente dessas tecnologias.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no commercial, proprietary or financial interest in the products or companies described in this article.
Figures








References
-
- Ntoutsi E, Fafalios P, Gadiraju U, Iosifidis V, Nejdl W, Vidal ME. Bias in data-driven artificial intelligence systems-an introductory survey. WIREs Data Mining Knowl Discov. 2020;10:e1356
-
- Alhashmi SF, Alshurideh M, Kurdi BA, Salloum SA. A systematic review of the factors affecting the artificial intelligence implementation in the health care sector; AICV 2020: Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision (AICV2020); Springer; 2020.
-
- Gandedkar NH, Vaid NR, Darendeliler MA, Premjani P, Ferguson DJ. The last decade in orthodontics a scoping review of the hits, misses and the near misses! Semin Orthod. 2019;25(4):339–355.
-
- Dreyer KJ, Hirschhorn D, Thrall JH, PACS M. A guide to the digital revolution. New York: Springer; 2006.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

