Efficacy and Safety of Lebrikizumab in Combination With Topical Corticosteroids in Adolescents and Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial (ADhere)
- PMID: 36630140
- PMCID: PMC9857439
- DOI: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2022.5534
Efficacy and Safety of Lebrikizumab in Combination With Topical Corticosteroids in Adolescents and Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial (ADhere)
Erratum in
-
Errors in Figure 2 and Table 2 Footnotes.JAMA Dermatol. 2023 Sep 1;159(9):1014. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.2199. JAMA Dermatol. 2023. PMID: 37466974 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Lebrikizumab (LEB), a high-affinity monoclonal antibody targeting interleukin (IL)-13, demonstrated efficacy and safety in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) during 16 weeks of monotherapy in a phase 2b trial, and two 52-week phase 3 trials.
Objective: To evaluate efficacy and safety of LEB combined with low- to mid-potency topical corticosteroids (TCS) in patients with moderate-to-severe AD.
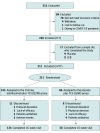
Design, setting, and participants: The ADhere trial was a 16-week randomized, double-blinded, placebo (PBO)-controlled, multicenter, phase 3 clinical trial conducted from February 3, 2020, to September 16, 2021. The study was conducted at 54 outpatient sites across Germany, Poland, Canada, and the US and included adolescent (aged ≥12 to <18 years weighing ≥40 kg) and adult patients with moderate-to-severe AD. The treatment allocation ratio was 2:1 (LEB:PBO).
Interventions: Overall, 211 patients were randomized to subcutaneous LEB (loading dose of 500 mg at baseline and week 2, followed by 250 mg every 2 weeks [Q2W] thereafter) or PBO Q2W in combination with TCS for 16 weeks.
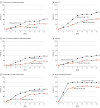
Main outcomes and measures: Efficacy analyses at week 16 included proportions of patients achieving Investigator's Global Assessment score of 0 or 1 (IGA [0,1]) with 2 or more points improvement from baseline, and 75% improvement in the Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI-75). Key secondary end points included evaluation of itch, itch interference on sleep, and quality of life. Safety assessments included monitoring adverse events (AEs).
Results: The mean (SD) age of patients was 37.2 (19.3) years, 103 (48.8%) patients were women, 31 (14.7%) patients were Asian, and 28 (13.3%) patients were Black/African American. At week 16, IGA (0,1) was achieved by 145 (41.2%) patients in the LEB+TCS group vs 66 (22.1%) receiving PBO+TCS (P = .01); corresponding proportions of patients achieving EASI-75 were 69.5% vs 42.2% (P < .001). The LEB+TCS group showed statistically significant improvements in all key secondary end points. Most treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were nonserious, mild or moderate in severity, and did not lead to study discontinuation. The TEAEs frequently reported in the LEB+TCS group included conjunctivitis (7 [4.8%]), headache (7 [4.8%]), hypertension (4 [2.8%]), injection site reactions (4 [2.8%]), and herpes infection (5 [3.4%]) vs 1.5% or less patient-reported frequencies in the PBO+TCS group. Similar frequencies of patient-reported serious AEs following LEB+TCS (n = 2, 1.4%) and PBO+TCS (n = 1, 1.5%).
Conclusions and relevance: In this randomized phase 3 clinical trial, LEB+TCS was associated with improved outcomes in adolescents and adults with moderate-to-severe AD compared with TCS alone, and safety was consistent with previously reported AD trials.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04250337.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

