Anti-LGI4 Antibody Is a Novel Juxtaparanodal Autoantibody for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
- PMID: 36631269
- PMCID: PMC9833819
- DOI: 10.1212/NXI.0000000000200081
Anti-LGI4 Antibody Is a Novel Juxtaparanodal Autoantibody for Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy
Abstract
Background and objectives: The objective of this study was to discover novel nodal autoantibodies in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP).
Methods: We screened for autoantibodies that bind to mouse sciatic nerves and dorsal root ganglia (DRG) using indirect immunofluorescence (IFA) assays with sera from 113 patients with CIDP seronegative for anti-neurofascin 155 and anticontactin-1 antibodies and 127 controls. Western blotting, IFA assays using HEK293T cells transfected with relevant antigen expression plasmids, and cell-based RNA interference assays were used to identify target antigens. Krox20 and Periaxin expression, both of which independently control peripheral nerve myelination, was assessed by quantitative real-time PCR after application of patient and control sera to Schwann cells.
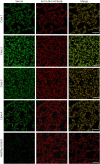
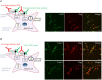
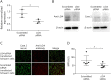
Results: Sera from 4 patients with CIDP, but not control sera, selectively bound to the nodal regions of sciatic nerves and DRG satellite glia (p = 0.048). The main immunoglobulin G (IgG) subtype was IgG4. IgG from these 4 patients stained a 60-kDa band on Western blots of mouse DRG and sciatic nerve lysates. These features indicated leucine-rich repeat LGI family member 4 (LGI4) as a candidate antigen. A commercial anti-LGI4 antibody and IgG from all 4 seropositive patients with CIDP showed the same immunostaining patterns of DRG and cultured rat Schwann cells and bound to the 60-kDa protein in Western blots of LGI4 overexpression lysates. IgG from 3 seropositive patients, but none from controls, bound to cells cotransfected with plasmids containing LGI4 and a disintegrin and metalloprotease domain-containing protein 22 (ADAM22), an LGI4 receptor. In cultured rat Schwann and human melanoma cells constitutively expressing LGI4, LGI4 siRNA effectively downregulated LGI4 and reduced patients' IgG binding compared with scrambled siRNA. Application of serum from a positive patient to Schwann cells expressing ADAM22 significantly reduced the expression of Krox20, but not Periaxin. Anti-LGI4 antibody-positive patients had a relatively old age at onset (mean age 58 years), motor weakness, deep and superficial sensory impairment with Romberg sign, and extremely high levels of CSF protein. Three patients showed subacute CIDP onset resembling Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Discussion: IgG4 anti-LGI4 antibodies are found in some elderly patients with CIDP who present subacute sensory impairment and motor weakness and are worth measuring, particularly in patients with symptoms resembling Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
