Distinct patterns of serum and urine macrophage migration inhibitory factor kinetics predict death in sepsis: a prospective, observational clinical study
- PMID: 36631486
- PMCID: PMC9834307
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-27506-6
Distinct patterns of serum and urine macrophage migration inhibitory factor kinetics predict death in sepsis: a prospective, observational clinical study
Abstract
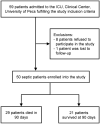
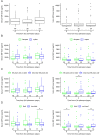
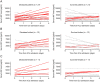
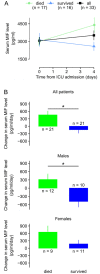
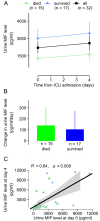
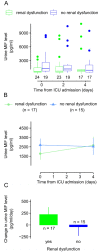
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) has been considered as a biomarker in sepsis, however the predictive value of the pattern of its kinetics in the serum and in the urine has remained unclarified. It is also unclear whether the kinetics of MIF are different between males and females. We conducted a single-center prospective, observational study with repeated measurements of MIF in serum and urine on days 0, 2, and 4 from admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) in 50 adult septic patients. We found that in patients who died within 90 days, there was an increase in serum MIF level from day 0 to 4, whereas in the survivors there was rather a decrease (p = 0.018). The kinetics were sex-dependent as the same difference in the pattern was present in males (p = 0.014), but not in females (p = 0.418). We also found that urine MIF was markedly lower in patients who died than in survivors of sepsis (p < 0.050). Urine MIF levels did not show temporal changes: there was no meaningful difference between day 0 and 4. These results suggest that kinetics of serum MIF during the initial days from ICU admission can predict death, especially in male patients. Additionally, lower urine MIF levels can also indicate death without showing meaningful temporal kinetics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increases in serum macrophage migration inhibitory factor in patients with severe sepsis predict early mortality.Shock. 2007 May;27(5):503-6. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e31802c024b. Shock. 2007. PMID: 17438455
-
Association between high levels of blood macrophage migration inhibitory factor, inappropriate adrenal response, and early death in patients with severe sepsis.Clin Infect Dis. 2007 May 15;44(10):1321-8. doi: 10.1086/514344. Epub 2007 Apr 5. Clin Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17443469 Clinical Trial.
-
Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Provides a Predictive Performance of Septic Acute Kidney Injury.Shock. 2022 May 1;57(5):666-671. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001918. Epub 2022 Feb 28. Shock. 2022. PMID: 35234206
-
Macrophage migration inhibitory factor levels correlate with fatal outcome in sepsis.Shock. 2004 Oct;22(4):309-13. doi: 10.1097/01.shk.0000140305.01641.c8. Shock. 2004. PMID: 15377884
-
Increased plasma thioredoxin levels in patients with sepsis: positive association with macrophage migration inhibitory factor.Intensive Care Med. 2010 Feb;36(2):336-41. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1640-z. Epub 2009 Sep 15. Intensive Care Med. 2010. PMID: 19756498 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Role of CD74 and D-Dopachrome Tautomerase in COVID-19: Insights from Transcriptomic and Serum Analyses.J Clin Med. 2023 Jul 31;12(15):5037. doi: 10.3390/jcm12155037. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37568438 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

