PDGF inhibits BMP2-induced bone healing
- PMID: 36631491
- PMCID: PMC9834334
- DOI: 10.1038/s41536-023-00276-5
PDGF inhibits BMP2-induced bone healing
Abstract
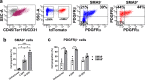
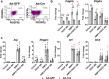
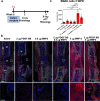
Bone regeneration depends on a pool of bone/cartilage stem/progenitor cells and signaling mechanisms regulating their differentiation. Using in vitro approach, we have shown that PDGF signaling through PDGFRβ inhibits BMP2-induced osteogenesis, and significantly attenuates expression of BMP2 target genes. We evaluated outcomes of treatment with two anabolic agents, PDGF and BMP2 using different bone healing models. Targeted deletion of PDGFRβ in αSMA osteoprogenitors, led to increased callus bone mass, resulting in improved biomechanical properties of fractures. In critical size bone defects BMP2 treatment increased proportion of osteoprogenitors, while the combined treatment of PDGF BB with BMP2 decreased progenitor number at the injury site. BMP2 treatment induced significant bone formation and increased number of osteoblasts, while in contrast combined treatment with PDGF BB decreased osteoblast numbers. This is in vivo study showing that PDGF inhibits BMP2-induced osteogenesis, but inhibiting PDGF signaling early in healing process does not improve BMP2-induced bone healing.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Recombinant human BMP2 and Adsorbable collagen sponge—Infuse provided by Medtronic to I.K. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Thomas, J. D. & Kehoe, J. L. In StatPearls (2021).
Grants and funding
- R01 AR055607/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR070813/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR055607/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)
- AR070813/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

