Outcomes Following Adalimumab Bio-originator to Biosimilar Switch-A Comparison Using Real-world Patient- and Physician-Reported Data in European Countries
- PMID: 36631636
- PMCID: PMC9834672
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-022-00526-w
Outcomes Following Adalimumab Bio-originator to Biosimilar Switch-A Comparison Using Real-world Patient- and Physician-Reported Data in European Countries
Abstract
Introduction: The aim of this work is to compare real-world outcomes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) receiving adalimumab (ADA) bio-originator (non-switchers) to those who had switched from ADA bio-originator to an ADA biosimilar (switchers) on the basis of the hypothesis that these outcomes would differ.
Methods: Data were drawn from the Adelphi RA Disease Specific Programme™, a point-in-time survey of physicians and their patients in Europe (France, Germany, Italy, Spain, UK) in 2020. Physicians completed a questionnaire for their next ten adult patients with RA, followed by four additional patients who had switched from ADA bio-originator to an ADA biosimilar (switchers). Physician- and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) for switchers and non-switchers were compared by propensity score matching.
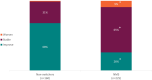
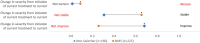
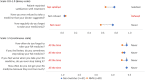
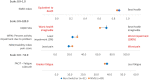
Results: Three hundred and three rheumatologists provided data for 160 non-switchers and 225 switchers, 140 patients provided data; 51 non-switchers, 89 switchers. According to physician-reported disease activity, non-switchers were more likely to improve on their current ADA treatment than switchers (68%, n = 108 vs. 26%, n = 59 p < 0.001) and less likely to worsen (1%, n = 2 vs. 9%, n = 20; p < 0.01). Physician-reported patient adherence was significantly lower amongst switchers versus non-switchers (0.66 vs. 0.78, respectively; p = 0.04). More non-switchers than switchers were reported by their physicians to be consistent in taking their RA medicine (p < 0.001). Compared with non-switchers, PRO measures indicated quality of life was worse (EQ-5D Visual Analogue Scale: 62.9 vs. 71.9; p < 0.001) and activity impairment was greater (Work Productivity Activity Index: 31.0 vs. 24.4; p = 0.02) for switchers, with trends for poorer health status and greater pain.
Conclusions: Non-medical switching in RA treatment may lead to unforeseen outcomes that should be considered by health decision-makers.
Keywords: Adalimumab; Biosimilar; Disease burden; Non-medical switching; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of non-medical switch from adalimumab bio-originator to SB5 biosimilar and from ABP501 adalimumab biosimilar to SB5 biosimilar in patients with chronic inflammatory arthropathies: a monocentric observational study.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2023 Mar;41(3):613-619. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/bf00j9. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 35916302
-
Real-World Experience of Adalimumab Biosimilar (ABP 501) Use in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Europe.Adv Ther. 2024 Jan;41(1):331-348. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02712-w. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 37957522 Free PMC article.
-
Real-World Experience with an Adalimumab Biosimilar (ABP 501) in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Psoriasis in Europe: Results from the Adelphi Disease Specific Programme.Rheumatol Ther. 2025 Jun;12(3):469-492. doi: 10.1007/s40744-025-00755-9. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Rheumatol Ther. 2025. PMID: 40064802 Free PMC article.
-
The Economic Impact of Originator-to-Biosimilar Non-medical Switching in the Real-World Setting: A Systematic Literature Review.Adv Ther. 2022 Jan;39(1):455-487. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01951-z. Epub 2021 Nov 15. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 34780028 Free PMC article.
-
Discontinuation and Switchback After Non-Medical Switching from Originator Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF) Inhibitors to Biosimilars: A Meta-Analysis of Real-World Studies from 2012 to 2018.Adv Ther. 2022 Aug;39(8):3711-3734. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02173-7. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35737227 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Biosimilars for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Riding the 2023 Wave [Podcast].Open Access Rheumatol. 2023 Oct 31;15:207-212. doi: 10.2147/OARRR.S443235. eCollection 2023. Open Access Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37927492 Free PMC article.
-
Defining a Framework for Sustainable Global Biosimilars Markets Using Findings from a Targeted Literature Review.BioDrugs. 2025 May;39(3):411-425. doi: 10.1007/s40259-025-00710-8. Epub 2025 Feb 26. BioDrugs. 2025. PMID: 40009310 Review.
-
Patient Experience with the SensoReady® Autoinjector Pen versus a Comparator Device: Results from a Canadian Patient Survey in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Crohn´s Disease.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024 Jun 5;18:1107-1118. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S455791. eCollection 2024. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2024. PMID: 38854477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé RBM, Bijlsma JWJ, Burmester GR, Dougados M, Kerschbaumer A, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2019 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):685–699. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216655. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

