Multimodal ultrasound-based carotid plaque risk biomarkers predict poor functional outcome in patients with ischemic stroke or TIA
- PMID: 36631804
- PMCID: PMC9835263
- DOI: 10.1186/s12883-023-03052-6
Multimodal ultrasound-based carotid plaque risk biomarkers predict poor functional outcome in patients with ischemic stroke or TIA
Abstract
Background: Carotid vulnerable plaque is an important risk factor for stroke occurrence and recurrence. However, the relationship between risk parameters related to carotid vulnerable plaque (plaque size, echogenicity, intraplaque neovascularization, and plaque stiffness) and neurological outcome after ischemic stroke or TIA is unclear. This study investigates the value of multimodal ultrasound-based carotid plaque risk biomarkers to predict poor short-term functional outcome after ischemic stroke or TIA.
Methods: This study was a single-center, prospective, continuous, cohort study to observe the occurrence of adverse functional outcomes (mRS 2-6/3-6) 90 days after ischemic stroke or TIA in patients, where the exposure factors in this study were carotid plaque ultrasound risk biomarkers and the risk factors were sex, age, disease history, and medication history. Patients with ischemic stroke or TIA (mRS ≤3) whose ipsilateral internal carotid artery stenosis was ≥50% within 30 days were included. All patients underwent multimodal ultrasound at baseline, including conventional ultrasound, superb microvascular imaging (SMI), and shear wave elastography (SWE). Continuous variables were divided into four groups at interquartile spacing for inclusion in univariate and multifactorial analyses. After completion of a baseline ultrasound, all patients were followed up at 90 days after ultrasound, and patient modified neurological function scores (mRSs) were recorded. Multivariate Cox regression and ROC curves were used to assess the risk factors and predictive power for predicting poor neurological function.
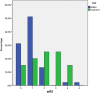
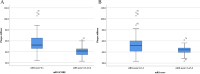
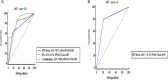
Results: SMI revealed that 20 (30.8%) patients showed extensive neovascularization in the carotid plaque, and 45 (69.2%) patients showed limited neovascularization in the carotid plaque. SWE imaging showed that the mean carotid plaque stiffness was 51.49 ± 18.34 kPa (23.19-111.39 kPa). After a mean follow-up of 90 ± 14 days, a total of 21 (32.3%) patients had a mRS of 2-6, and a total of 10 (15.4%) patients had a mRS of 3-6. Cox regression analysis showed that the level of intraplaque neovascularization and plaque stiffness were independent risk factors for a mRS of 2-6, and the level of intraplaque neovascularization was an independent risk factor for a mRS of 3-6. After correcting for confounders, the HR of intraplaque neovascularization level and plaque stiffness predicting a mRS 2-6 was 3.06 (95% CI 1.05-12.59, P = 0.041) and 0.51 (95% CI 0.31-0.83, P = 0.007), respectively; the HR of intraplaque neovascularization level predicting a mRS 3-6 was 6.11 (95% CI 1.19-31.45, P = 0.031). For ROC curve analysis, the mRSs for intraplaque neovascularization level, plaque stiffness, and combined application to predict 90-day neurological outcome ranged from 2 to 6, with AUCs of 0.73 (95% CI 0.59-0.87), 0.76 (95% CI 0.64-0.89) and 0.85 (95% CI 0.76-0.95), respectively. The mRSs for the intraplaque neovascularization level to predict 90-day neurological outcome ranged from 3 to 6, with AUCs of 0.79 (95% CI 0.63-0.95).
Conclusion: Intraplaque neovascularization level and plaque stiffness may be associated with an increased risk of poor short-term functional outcome after stroke in patients with recent anterior circulation ischemic stroke due to carotid atherosclerosis. The combined application of multiple parameters has efficacy in predicting poor short-term functional outcome after stroke.
Keywords: Carotid plaque; Multimodal ultrasound; Shear wave elastography; Stroke; Superb microvascular imaging.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advanced ultrasound methods in assessment of carotid plaque instability: a prospective multimodal study.BMC Neurol. 2020 Jan 29;20(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-1620-z. BMC Neurol. 2020. PMID: 31996153 Free PMC article.
-
Carotid Plaque Characteristics Predict Recurrent Ischemic Stroke and TIA: The PARISK (Plaque At RISK) Study.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022 Oct;15(10):1715-1726. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2022.04.003. Epub 2022 Jun 15. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2022. PMID: 36202450
-
Intraplaque Microvascular Flow Signal in Superb Microvascular Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Carotid Plaque Imaging in Patients with Atheromatous Carotid Artery Stenosis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018 Dec;27(12):3529-3534. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.08.017. Epub 2018 Sep 7. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 30197167
-
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound to Assess Carotid Intraplaque Neovascularization.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020 Mar;46(3):466-478. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2019.10.020. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 31791553
-
Non-traditional lipid parameters as potential predictors of carotid plaque vulnerability and stenosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke.Neurol Sci. 2023 Mar;44(3):835-843. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-06472-3. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36301362 Review.
Cited by
-
Relationship between maximum carotid plaque area and prognosis of patients with acute ischaemic stroke.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Oct;193(5):2501-2507. doi: 10.1007/s11845-024-03739-w. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38890259
-
Independent predictors of ischemic stroke: a comprehensive scan of the internal carotid and vertebrobasilar systems.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025 Apr 1;15(4):2827-2838. doi: 10.21037/qims-24-1763. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2025. PMID: 40235781 Free PMC article.
-
Napkin-ring sign plaques are associated with cerebral small vessel disease.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Mar 21;30(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02371-3. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40114260 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological and biomechanical characteristics of carotid plaques with mild stenosis using ultrafast and high-definition ultrasonography.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jul 14. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11816-6. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40658201
-
Incremental clinical value of intraplaque neovascularization in predicting recurrent ischemic stroke.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2025 Feb;12(2):291-299. doi: 10.1002/acn3.52255. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2025. PMID: 39556520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kang DO, Eo JS, Park EJ, et al. Stress-associated neurobiological activity is linked with acute plaque instability via enhanced macrophage activity: a prospective serial 18F-FDG-PET/CT imaging assessment. Eur Heart J. 2021;18:ehaa1095. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

