Harnessing electromagnetic fields to assist bone tissue engineering
- PMID: 36631880
- PMCID: PMC9835389
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-03217-z
Harnessing electromagnetic fields to assist bone tissue engineering
Abstract
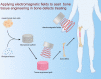
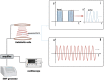
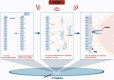
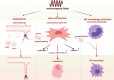
Bone tissue engineering (BTE) emerged as one of the exceptional means for bone defects owing to it providing mechanical supports to guide bone tissue regeneration. Great advances have been made to facilitate the success of BTE in regenerating bone within defects. The use of externally applied fields has been regarded as an alternative strategy for BTE. Electromagnetic fields (EMFs), known as a simple and non-invasive therapy, can remotely provide electric and magnetic stimulation to cells and biomaterials, thus applying EMFs to assist BTE would be a promising strategy for bone regeneration. When combined with BTE, EMFs improve cell adhesion to the material surface by promoting protein adsorption. Additionally, EMFs have positive effects on mesenchymal stem cells and show capabilities of pro-angiogenesis and macrophage polarization manipulation. These advantages of EMFs indicate that it is perfectly suitable for representing the adjuvant treatment of BTE. We also summarize studies concerning combinations of EMFs and diverse biomaterial types. The strategy of combining EMFs and BTE receives encouraging outcomes and holds a promising future for effectively treating bone defects.
Keywords: Bone regeneration; Bone tissue engineering; Electromagnetic fields; Osteogenesis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- McDermott AM, Herberg S, Mason DE, Collins JM, Pearson HB, Dawahare JH, Tang R, Patwa AN, Grinstaff MW, Kelly DJ, et al. Recapitulating bone development through engineered mesenchymal condensations and mechanical cues for tissue regeneration. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(495):eaav7756. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav7756. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koons GL, Diba M, Mikos AG. Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nat Rev Mater. 2020;5(8):584–603. doi: 10.1038/s41578-020-0204-2. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

