Soya saponins and prebiotics alter intestinal functions in Ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta)
- PMID: 36632013
- PMCID: PMC10404481
- DOI: 10.1017/S000711452200383X
Soya saponins and prebiotics alter intestinal functions in Ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta)
Abstract
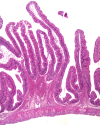
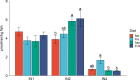
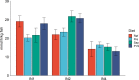
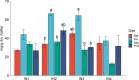
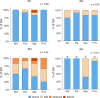
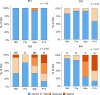
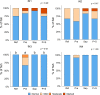
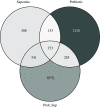
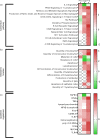
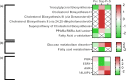
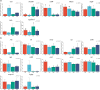
A 5-week feeding trial was conducted in the cleaner fish Ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta) for a better understanding of the basic biology of the intestinal functions and health in this stomach less species. During the trial, Ballan wrasse was fed either a reference diet, the reference diet supplemented with (i) a commercial prebiotic (Aquate™ SG, 0·4 %) expected to have beneficial effects, (ii) soya saponins (0·7 %) expected to induce inflammation or (iii) a combination of the prebiotics and the soya saponins to find a remedy for gut inflammation. Blood, intestinal tissue and gut content from four consecutive intestinal segments (IN1 - IN4) were collected. No significant differences in fish growth were observed between the four dietary groups. Saponin supplementation, both alone and in combination with prebiotics, increased weight index of IN2 and IN3 and decreased blood plasma glucose, cholesterol and total protein. Dry matter of intestinal content and activity of digestive enzymes were not affected by diet. Histomorphological analyses revealed a progressing inflammation with increased infiltration by immune cells particularly into the distal parts of the intestine in fish fed diets with saponins, both alone and in combination with prebiotics. Gene expression profiles obtained by RNA sequencing and quantitative PCR mirrored the histological and biochemical changes induced by the saponin load. The study demonstrated that Ballan wrasse gut health and digestive function may be markedly affected by feed ingredients containing antinutrients.
Keywords: Antinutrients; Ballan wrasse; Cleaner fish; Gut health; Prebiotics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Digestive and immune functions in the intestine of wild Ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta).Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2021 Oct;260:111011. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2021.111011. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34174428
-
Welfare and performance of ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta) reared at two different temperatures after a preparatory feeding trial with enhanced dietary eicosapentaenoic acid.J Fish Biol. 2023 Nov;103(5):906-923. doi: 10.1111/jfb.15482. Epub 2023 Jul 6. J Fish Biol. 2023. PMID: 37321978
-
Loss of stomach, loss of appetite? Sequencing of the ballan wrasse (Labrus bergylta) genome and intestinal transcriptomic profiling illuminate the evolution of loss of stomach function in fish.BMC Genomics. 2018 Mar 6;19(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4570-8. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29510660 Free PMC article.
-
Sustainable production and use of cleaner fish for the biological control of sea lice: recent advances and current challenges.Vet Rec. 2018 Sep 29;183(12):383. doi: 10.1136/vr.104966. Epub 2018 Jul 30. Vet Rec. 2018. PMID: 30061113 Review.
-
A review of potential pathogens of sea lice and the application of cleaner fish in biological control.Pest Manag Sci. 2002 Jun;58(6):546-58. doi: 10.1002/ps.509. Pest Manag Sci. 2002. PMID: 12138621 Review.
References
-
- Brooker AJ, Papadopoulou A, Gutierrez C, et al. (2018) Sustainable production and use of cleaner fish for the biological control of sea lice: recent advances and current challenges. Vet Rec 183, 383. - PubMed
-
- Skiftesvik AB, Blom G, Agnalt AL, et al. (2014) Wrasse (Labridae) as cleaner fish in salmonid aquaculture – the Hardangerfjord as a case study. Mar Biol Res 10, 289–300.
-
- Gonzalez EB & de Boer F (2017) The development of the Norwegian wrasse fishery and the use of wrasses as cleaner fish in the salmon aquaculture industry. Fish Sci 83, 661–670.
-
- Overton K, Dempster T, Oppedal F, et al. (2019) Salmon lice treatments and salmon mortality in Norwegian aquaculture: a review. Rev Aquacult 11, 1398–1417.
-
- Aaen SM, Helgesen KO, Bakke MJ, et al. (2015) Drug resistance in sea lice: a threat to salmonid aquaculture. Trends Parasitol 31, 72–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

