The role of dietary antioxidants in type 2 diabetes and neurodegenerative disorders: An assessment of the benefit profile
- PMID: 36632095
- PMCID: PMC9826852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12698
The role of dietary antioxidants in type 2 diabetes and neurodegenerative disorders: An assessment of the benefit profile
Abstract
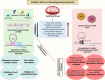
Healthy diet is vital to cellular health. The human body succumbs to numerous diseases which afflict severe economic and psychological burdens on the patient and family. Oxidative stress is a possible crucial regulator of various pathologies, including type 2 diabetes and neurodegenerative diseases. It generates reactive oxygen species (ROS) that trigger the dysregulation of essential cellular functions, ultimately affecting cellular health and homeostasis. However, lower levels of ROS can be advantageous and are implicated in a variety of signaling pathways. Due to this dichotomy, the terms oxidative "eustress," which refers to a good oxidative event, and "distress," which can be hazardous, have developed. ROS affects multiple signaling pathways, leading to compromised insulin secretion, insulin resistance, and β-cell dysfunction in diabetes. ROS is also associated with increased mitochondrial dysfunction and neuroinflammation, aggravating neurodegenerative conditions in the body, particularly with age. Treatment includes drugs/therapies often associated with dependence, side effects including non-selectivity, and possible toxicity, particularly in the long run. It is imperative to explore alternative medicines as an adjunct therapy, utilizing natural remedies/resources to avoid all the possible harms. Antioxidants are vital components of our body that fight disease by reducing oxidative stress or nullifying the excess toxic free radicals produced under various pathological conditions. In this review, we focus on the antioxidant effects of components of dietary foods such as tea, coffee, wine, oils, and honey and the role and mechanism of action of these antioxidants in alleviating type 2 diabetes and neurodegenerative disorders. We aim to provide information about possible alternatives to drug treatments used alone or combined to reduce drug intake and encourage the consumption of natural ingredients at doses adequate to promote health and combat pathologies while reducing unwanted risks and side effects.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Diet; Neurodegenerative diseases; Reactive oxygen species; Therapeutics; Type 2 diabetes.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Halliwell B. Free radicals and antioxidants - quo vadis? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2011;32:125–130. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

