Relapsing Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease With Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
- PMID: 36632255
- PMCID: PMC9827933
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32344
Relapsing Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease With Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis
Abstract
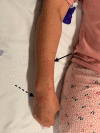
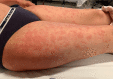
Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease is a rare, benign, and self-limited disease of uncertain etiology, affecting mostly young female patients. It usually manifests as posterior cervical lymphadenopathy and fever. Its diagnosis is based on typical histopathological changes after the exclusion of other diseases such as lupus, lymphoma, or infectious lymphadenitis. The authors present a 47-year-old female patient with recurring episodes of high fever, urticarial rash, myalgia, arthralgia, fatigue, sore throat, and generalized lymphadenopathy. Blood tests showed increased inflammatory parameters and positive antinuclear antibodies. In the two times the patient was admitted to the hospital there were no infectious agents isolated. The patient didn't fulfill the criteria for diagnosis of lupus or any other autoimmune disease and there was also no evidence of lymphoma or other neoplastic diseases. A positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) was performed at the first and second hospitalizations, showing generalized lymphadenopathy. At the first hospitalization, a mediastinal lymph node biopsy was obtained, excluding lymphoproliferative or granulomatous disease. During the course of the second hospitalization, a cervical lymph node was excised for biopsy, the histopathological changes of which suggested the diagnosis of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. The clinical course was complicated by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, with a significant increase in inflammatory markers and liver dysfunction. The patient was treated with prednisolone 1 mg/kg/day, with complete resolution of clinical and biochemical changes.
Keywords: cervical lymphadenopathy; fever; hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; histiocytic necrotizing lymphadenitis; kikuchi-fujimoto disease; migratory arthralgia; urticarial rash.
Copyright © 2022, Valente et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: a review. Perry AM, Choi SM. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018;142:1341–1346. - PubMed
-
- Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease: analysis of 244 cases. Kucukardali Y, Solmazgul E, Kunter E, Oncul O, Yildirim S, Kaplan M. Clin Rheumatol. 2007;26:50–54. - PubMed
-
- Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease. Hutchinson CB, Wang E. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134:289–293. - PubMed
-
- A challenging case of Kikuchi-Fujimoto disease with systemic lupus erythematosus complicated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a young man. Pradhan S, Sirka CS, Dash G, Sahu K, Rout AN. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2021;87:78–82. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
