Urinary Tract Infection Induced Delirium in Elderly Patients: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36632270
- PMCID: PMC9827929
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.32321
Urinary Tract Infection Induced Delirium in Elderly Patients: A Systematic Review
Abstract
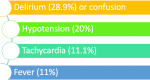
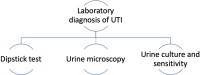
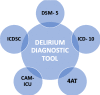
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is common in older adults, mainly due to several age-related risk factors. Symptoms of UTI are atypical in the elderly population, like hypotension, tachycardia, urinary incontinence, poor appetite, drowsiness, frequent falls, and delirium. UTI manifests more commonly and specifically for this age group as delirium or confusion in the absence of a fever. This systematic review aims to highlight the relationship between UTI and delirium in the elderly population by understanding the pathologies individually and collectively. A systematic review is conducted by searching PubMed with regular keywords and major Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) keywords, Science Direct, and Google Scholar. The inclusion criteria consisted of studies based on male and female human populations above the age of 65 in the English language, available in full text published between 2017 and 2022. However, the exclusion criteria were animal studies, clinical trials, literature published before 2017, and papers published in any other language except English. A total of 106 articles were identified, and nine final studies were selected after a quality assessment, following which a valid relationship between delirium and UTI was identified in this systematic review.
Keywords: asymptomatic bacteriuria; atypical presentation; delirium; elderly; geriatrics; infection induced delirium; urinary tract infection; urinary tract infection symptoms in elderly; urine infection.
Copyright © 2022, Dutta et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Urinary tract infections in a geriatric sub-acute ward-health correlates and atypical presentations. Wojszel ZB, Toczyńska-Silkiewicz M. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-018-0099-2. Eur Geriatr Med. 2018;9:659–667. - PMC - PubMed
-
- The scientific evidence for a potential link between confusion and urinary tract infection in the elderly is still confusing - a systematic literature review. Mayne S, Bowden A, Sundvall PD, Gunnarsson R. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-019-1049-7. BMC Geriatr. 2019;19:32. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Predisposing and precipitating factors for delirium in community-dwelling older adults admitted to hospital with this condition: a prospective case series. Magny E, Le Petitcorps H, Pociumban M, et al. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193034 PLoS One. 2018;13:0. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
